Epigenetic Regulation of Dental Pulp Stem Cell Fate
- PMID: 33149742
- PMCID: PMC7603635
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8876265
Epigenetic Regulation of Dental Pulp Stem Cell Fate
Abstract
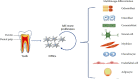
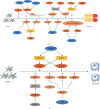
Epigenetic regulation, mainly involving DNA methylation, histone modification, and noncoding RNAs, affects gene expression without modifying the primary DNA sequence and modulates cell fate. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental pulp, also called dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs), exhibit multipotent differentiation capacity and can promote various biological processes, including odontogenesis, osteogenesis, angiogenesis, myogenesis, and chondrogenesis. Over the past decades, increased attention has been attracted by the use of DPSCs in the field of regenerative medicine. According to a series of studies, epigenetic regulation is essential for DPSCs to differentiate into specialized cells. In this review, we summarize the mechanisms involved in the epigenetic regulation of the fate of DPSCs.
Copyright © 2020 Dan Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanical Signaling in Dental Pulp Stem Cells.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Oct 31;28(10):274. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2810274. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 37919075 Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of dental pulp stem cells and its potential in regenerative endodontics.World J Stem Cells. 2021 Nov 26;13(11):1647-1666. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i11.1647. World J Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 34909116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elucidating epigenetic mechanisms governing odontogenic differentiation in dental pulp stem cells: an in-depth exploration.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 May 28;12:1394582. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1394582. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38863943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alcohol-induced suppression of KDM6B dysregulates the mineralization potential in dental pulp stem cells.Stem Cell Res. 2016 Jul;17(1):111-21. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2016.05.021. Epub 2016 May 31. Stem Cell Res. 2016. PMID: 27286573 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Methylation and Histone Modification in Dental-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022 Dec;18(8):2797-2816. doi: 10.1007/s12015-022-10413-0. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022. PMID: 35896859 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of EZH2 inhibitor, trichostatin A, and 5-azacytidine combinatorial treatment on osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 8;10(12):e32553. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32553. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39183840 Free PMC article.
-
Dental Pulp Stem Cell Heterogeneity: Finding Superior Quality "Needles" in a Dental Pulpal "Haystack" for Regenerative Medicine-Based Applications.Stem Cells Int. 2022 Jan 4;2022:9127074. doi: 10.1155/2022/9127074. eCollection 2022. Stem Cells Int. 2022. PMID: 35027930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Genetic Determinants of Dental Maturation in Children.J Dent Res. 2023 Mar;102(3):349-356. doi: 10.1177/00220345221132268. Epub 2022 Nov 27. J Dent Res. 2023. PMID: 36437532 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a Stemness-Optimized Purification Method for Human Dental-Pulp Stem Cells: An Approach to Standardization.Cells. 2022 Oct 12;11(20):3204. doi: 10.3390/cells11203204. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36291072 Free PMC article.
-
Adult Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Oral Cavity and Surrounding Areas: Types and Biomedical Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 9;15(8):2109. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082109. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631323 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

