Epigenetic Regulation of Dental Pulp Stem Cell Fate
- PMID: 33149742
- PMCID: PMC7603635
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8876265
Epigenetic Regulation of Dental Pulp Stem Cell Fate
Abstract
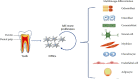
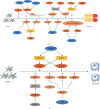
Epigenetic regulation, mainly involving DNA methylation, histone modification, and noncoding RNAs, affects gene expression without modifying the primary DNA sequence and modulates cell fate. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental pulp, also called dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs), exhibit multipotent differentiation capacity and can promote various biological processes, including odontogenesis, osteogenesis, angiogenesis, myogenesis, and chondrogenesis. Over the past decades, increased attention has been attracted by the use of DPSCs in the field of regenerative medicine. According to a series of studies, epigenetic regulation is essential for DPSCs to differentiate into specialized cells. In this review, we summarize the mechanisms involved in the epigenetic regulation of the fate of DPSCs.
Copyright © 2020 Dan Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

