Investigation of the potential regulator proteins associated with the expression of major surface protein and dentilisin in Treponema denticola
- PMID: 33149843
- PMCID: PMC7586716
- DOI: 10.1080/20002297.2020.1829404
Investigation of the potential regulator proteins associated with the expression of major surface protein and dentilisin in Treponema denticola
Erratum in
-
Correction.J Oral Microbiol. 2021 Mar 18;13(1):1892419. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2021.1892419. eCollection 2021. J Oral Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34925710 Free PMC article.
Abstract
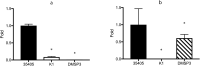
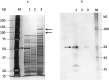
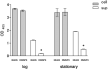
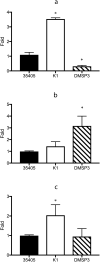
Objective Treponema denticola is involved in 'chronic' periodontitis pathogenesis. The mechanism underlying the regulation of the expression of its virulence factors, such as major surface protein (Msp) and prolyl-phenylalanine specific protease (dentilisin) is yet to be clarified. We determined the gene expression profiles of Msp- and dentilisin-deficient mutants of T. denticola to identify the regulation network of gene expression concomitant with the inactivation of these virulence genes. Methods Gene expression profiles of T. denticola ATCC 35405 (wild type), dentilisin-deficient mutant K1, and msp-deficient mutant DMSP3 were determined using DNA microarray analysis and quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR). Msp and dentilisin protein levels were determined by immunoblotting and proteolytic activity assays. Results In addition to several differentially expressed genes, dentilisin expression was reduced in DMSP3; msp expression was significantly reduced in K1 (p < 0.05), both at the gene and protein levels. To identify the regulatory system involved, the expression levels of the potential regulators whose expression showed changes in the mutants were evaluated using qRT-PCR. Transcriptional regulators TDE_0127 and TDE_0814 were upregulated in K1, and the potential repressor, TDE_0344, was elevated in DMSP3. Conclusions Dentilisin and Msp expression were interrelated, and gene expression regulators, such as TDE_0127, may be involved in their regulation.
Keywords: DNA-binding protein; Treponema denticola; dentilisin; gene expression; major surface protein; repressor.
© 2020 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kinane DF, Stathopoulou PG, Papapanou PN.. Periodontal diseases. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17038. - PubMed
-
- Socransky SS, Haffajee AD, Cugini MA, et al. Microbial complexes in subgingival plaque. J Clin Periodontol. 1998;25(2):134–144. - PubMed
-
- Ellen RP, Galimanas VB. Spirochetes at the forefront of periodontal infections. Periodontol. 2005;38:13–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
