Effect of biologic materials on the outcomes of horizontal alveolar ridge augmentation: A retrospective study
- PMID: 33150685
- PMCID: PMC8019766
- DOI: 10.1002/cre2.343
Effect of biologic materials on the outcomes of horizontal alveolar ridge augmentation: A retrospective study
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to investigate if the addition of biologic agents to a particulate bone graft enhances horizontal ridge augmentation outcomes in terms of bone dimensions, bone density, and successful implant placement.
Materials and methods: A retrospective chart review was done to assess the clinical and radiographic outcomes in 52 horizontal ridge augmentation sites in 43 patients. Information was gathered regarding surgical technique, type of graft material, biologic agents used (PRP or rhPDGF-BB), method of space maintenance, and achieved alveolar ridge width and bone density changes as quantified on CBCT scans.
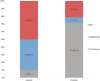
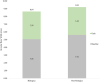
Results: The use of tenting screws, a resorbable membrane, and a combination of particulate allogenic and xenogenic bone graft material provided an average horizontal bone gain of 3.6 mm in the 52 augmented sites. There was no statistically significant difference observed in the amount of horizontal bone gain between sites treated with the addition of biologic agents (n = 21), or with a particulate bone graft alone (n = 31). A marginally statistically significant difference was found in the density of the grafted bone with the addition of biologics (p value = .0653).
Conclusion: The addition of biologic agents to the graft materials did not have a significant effect on the amount of horizontal bone gain or successful implant placement; however, it marginally enhanced the bone density of the grafted area.
Keywords: PRP; biologics; bone density; bone gain; horizontal ridge augmentation; radiographic evaluation; rhPDGF-BB.
© 2020 The Authors. Clinical and Experimental Dental Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Aghaloo, T. L. , & Moy, P. K. (2007). Which hard tissue augmentation techniques are the most successful in furnishing bony support for implant placement? The International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants 22, 49–70. - PubMed
-
- Aimetti, M. , Manavella, V. , Corano, L. , Ercoli, E. , Bignardi, C. , & Romano, F. (2018). Three‐dimensional analysis of bone remodeling following ridge augmentation of compromised extraction sockets in periodontitis patients: A randomized controlled study. Clinical Oral Implants Research, 29(2), 202–214. 10.1111/clr.13099 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alissa, R. , Esposito, M. , Horner, K. , & Oliver, R. (2010). The influence of platelet‐rich plasma on the healing of extraction sockets: An explorative randomised clinical trial. European Journal of Oral Implantology, 3(2), 121–134. - PubMed
-
- Badylak, S. , Bartold, P. , Giannobile, W. , Katagiri, W. , Nares, S. , Rios, H. , … Wikesjö, U. (2017). Biologics and cell therapy tissue engineering approaches for the management of the edentulous maxilla: A systematic review. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants. 10.11607/jomi.16suppl.g4 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

