SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors: identification of anti-SARS-CoV-2 Mpro compounds from FDA approved drugs
- PMID: 33150855
- PMCID: PMC7651494
- DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1842807
SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors: identification of anti-SARS-CoV-2 Mpro compounds from FDA approved drugs
Abstract
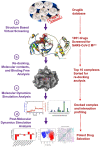
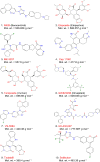
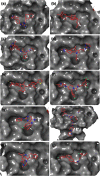
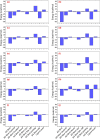
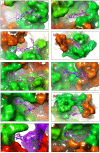
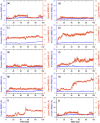
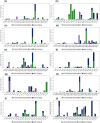
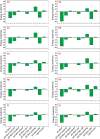
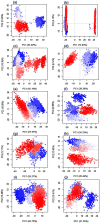
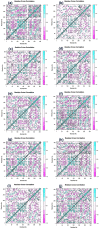
Recent outbreak of COVID-19 pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome-Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) has raised serious global concern for public health. The viral main 3-chymotrypsin-like cysteine protease (Mpro), known to control coronavirus replication and essential for viral life cycle, has been established as an essential drug discovery target for SARS-CoV-2. Herein, we employed computationally screening of Druglib database containing FDA approved drugs against active pocket of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro using MTiopen screen web server, yields a total of 1051 FDA approved drugs with docking energy >-7 kcal/mol. The top 10 screened potential compounds against SARS-CoV-2 Mpro were then studied by re-docking, binding affinity, intermolecular interaction, and complex stability via 100 ns all atoms molecular dynamics (MD) simulation followed by post-simulation analysis, including end point binding free energy, essential dynamics, and residual correlation analysis against native crystal structure ligand N3 inhibitor. Based on comparative molecular simulation and interaction profiling of the screened drugs with SARS-CoV-2 Mpro revealed R428 (-10.5 kcal/mol), Teniposide (-9.8 kcal/mol), VS-5584 (-9.4 kcal/mol), and Setileuton (-8.5 kcal/mol) with stronger stability and affinity than other drugs and N3 inhibitor; and hence, these drugs are advocated for further validation using in vitro enzyme inhibition and in vivo studies against SARS-CoV-2 infection.Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
Keywords: COVID-19; drug repurposing; molecular docking; molecular dynamics simulation; structure-based virtual screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploring epigenetic drugs as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease: a docking and MD simulation study.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Aug;42(13):6892-6903. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2236714. Epub 2023 Jul 17. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 37458994
-
Screening of plant-based natural compounds as a potential COVID-19 main protease inhibitor: an in silico docking and molecular dynamics simulation approach.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022 Feb;40(2):696-711. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1817787. Epub 2020 Sep 8. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 32897138 Free PMC article.
-
Computational insights into tetracyclines as inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 Mpro via combinatorial molecular simulation calculations.Life Sci. 2020 Sep 15;257:118080. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118080. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32653520 Free PMC article.
-
In silico molecular docking, dynamics simulation and repurposing of some VEGFR-2 inhibitors based on the SARS-CoV-2-main-protease inhibitor N3.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023 Nov;41(19):9267-9281. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2022.2148000. Epub 2022 Nov 18. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023. PMID: 36399002 Review.
-
COVID-19: inflammatory responses, structure-based drug design and potential therapeutics.Mol Divers. 2022 Feb;26(1):629-645. doi: 10.1007/s11030-020-10176-1. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Mol Divers. 2022. PMID: 33400086 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Review on development of potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (MPro).Futur J Pharm Sci. 2022;8(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s43094-022-00423-7. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Futur J Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35756354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pyrazolone-type compounds: synthesis and in silico assessment of antiviral potential against key viral proteins of SARS-CoV-2.RSC Adv. 2022 May 27;12(25):16054-16070. doi: 10.1039/d2ra02542f. eCollection 2022 May 23. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35733695 Free PMC article.
-
Computational and In Vitro Experimental Investigations Reveal Anti-Viral Activity of Licorice and Glycyrrhizin against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Nov 24;14(12):1216. doi: 10.3390/ph14121216. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34959616 Free PMC article.
-
A Study of 3CLpros as Promising Targets against SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2.Microorganisms. 2021 Apr 3;9(4):756. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9040756. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33916747 Free PMC article.
-
The Inhibitory Potential of Ferulic Acid Derivatives against the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics, and ADMET Evaluation.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 25;10(8):1787. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081787. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35892687 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bharadwaj, S., Lee, K. E., Dwivedi, V. D., Yadava, U., Nees, M., & Kang, S. G. (2020). Density functional theory and molecular dynamics simulation support Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids as broad range antagonist of matrix metalloproteinases. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 311, 113322. 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113322 - DOI
-
- Bharadwaj, S., Lee, K. E., Dwivedi, V. D., Yadava, U., Panwar, A., Lucas, S. J., Pandey, A., & Kang, S. G. (2019). Discovery of Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids as potential inhibitors against Dengue virus NS2B-NS3 protease. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 19059. 10.1038/s41598-019-55723-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bharadwaj, S., Rao, A. K., Dwivedi, V. D., Mishra, S. K., & Yadava, U. (2020). Structure-based screening and validation of bioactive compounds as Zika virus Methyltransferase (MTase) inhibitors through first-principle density functional theory, classical molecular simulation and QM/MM affinity estimation. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 1–20. 10.1080/07391102.2020.1747545 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bowers, K. J., Chow, D. E., Xu, H., Dror, R. O., Eastwood, M. P., Gregersen, B. A., Sacerdoti, F. D.Shaw, D. E., Shan, Y., Salmon, J. K., Moraes, M. A., Kolossvary, I., Klepeis, J. L. (2006). Scalable algorithms for molecular dynamics simulations on commodity clusters. Paper presented at the SC’06: Proceedings of the 2006 ACM/IEEE Conference on Supercomputing. IEEE.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
