COVID-19-related mortality in kidney transplant and dialysis patients: results of the ERACODA collaboration
- PMID: 33151337
- PMCID: PMC7665620
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa261
COVID-19-related mortality in kidney transplant and dialysis patients: results of the ERACODA collaboration
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: COVID-19-related mortality in kidney transplant and dialysis patients: results of the ERACODA collaboration.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021 Sep 27;36(10):1962. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfab028. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021. PMID: 34075410 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Patients on kidney replacement therapy comprise a vulnerable population and may be at increased risk of death from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Currently, only limited data are available on outcomes in this patient population.
Methods: We set up the ERACODA (European Renal Association COVID-19 Database) database, which is specifically designed to prospectively collect detailed data on kidney transplant and dialysis patients with COVID-19. For this analysis, patients were included who presented between 1 February and 1 May 2020 and had complete information available on the primary outcome parameter, 28-day mortality.
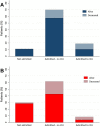
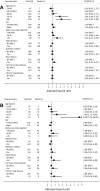
Results: Of the 1073 patients enrolled, 305 (28%) were kidney transplant and 768 (72%) dialysis patients with a mean age of 60 ± 13 and 67 ± 14 years, respectively. The 28-day probability of death was 21.3% [95% confidence interval (95% CI) 14.3-30.2%] in kidney transplant and 25.0% (95% CI 20.2-30.0%) in dialysis patients. Mortality was primarily associated with advanced age in kidney transplant patients, and with age and frailty in dialysis patients. After adjusting for sex, age and frailty, in-hospital mortality did not significantly differ between transplant and dialysis patients [hazard ratio (HR) 0.81, 95% CI 0.59-1.10, P = 0.18]. In the subset of dialysis patients who were a candidate for transplantation (n = 148), 8 patients died within 28 days, as compared with 7 deaths in 23 patients who underwent a kidney transplantation <1 year before presentation (HR adjusted for sex, age and frailty 0.20, 95% CI 0.07-0.56, P < 0.01).
Conclusions: The 28-day case-fatality rate is high in patients on kidney replacement therapy with COVID-19 and is primarily driven by the risk factors age and frailty. Furthermore, in the first year after kidney transplantation, patients may be at increased risk of COVID-19-related mortality as compared with dialysis patients on the waiting list for transplantation. This information is important in guiding clinical decision-making, and for informing the public and healthcare authorities on the COVID-19-related mortality risk in kidney transplant and dialysis patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; dialysis; kidney; mortality; transplantation.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Weekly Epidemiological Update and Weekly ... (1 September 2020, date last accessed)
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM.. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020; 323: 1239. - PubMed
-
- COVID-19 Cases and Case Fatality Rate by age. https://ec.europa.eu/knowledge4policy/sites/know4pol/files/jrc120420_cov... (6 October 2020, date last accessed)

