Lysophosphatidic Acid Signalling in Nervous System Development and Function
- PMID: 33151452
- PMCID: PMC11420905
- DOI: 10.1007/s12017-020-08630-2
Lysophosphatidic Acid Signalling in Nervous System Development and Function
Abstract
One class of molecules that are now coming to be recognized as essential for our understanding of the nervous system are the lysophospholipids. One of the major signaling lysophospholipids is lysophosphatidic acid, also known as LPA. LPA activates a variety of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) leading to a multitude of physiological responses. In this review, I describe our current understanding of the role of LPA and LPA receptor signaling in the development and function of the nervous system, especially the central nervous system (CNS). In addition, I highlight how aberrant LPA receptor signaling may underlie neuropathological conditions, with important clinical application.
Keywords: Autotaxin; Axon guidance; Cortical development; LPA receptors; Lysophospholipid; Neuropathic pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
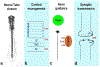

References
-
- An S, Bleu T, Hallmark OG, & Goetzl EJ (1998). Characterization of a novel subtype of human G protein-coupled receptor for lysophosphatidic acid. J. Biol. Chem, 273(14), 7906–7910. - PubMed
-
- Aoki J, Inoue A, & Okudaira S. (2008). Two pathways for lysophosphatidic acid production. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1781(9), 513–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

