MiR-21 mediates the protection of kaempferol against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte injury via promoting Notch1/PTEN/AKT signaling pathway
- PMID: 33151961
- PMCID: PMC7644004
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241007
MiR-21 mediates the protection of kaempferol against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte injury via promoting Notch1/PTEN/AKT signaling pathway
Abstract
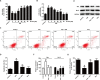
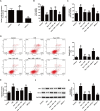
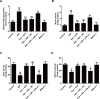
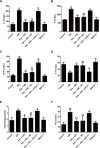
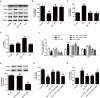
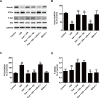
Kaempferol, a natural flavonoid compound, possesses potent myocardial protective property in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R), but the underlying mechanism is not well understood. The present study was aimed to explore whether miR-21 contributes to the cardioprotective effect of kaempferol on hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R)-induced H9c2 cell injury via regulating Notch/phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN)/Akt signaling pathway. Results revealed that kaempferol obviously attenuates H/R-induced the damages of H9c2 cells as evidence by the up-regulation of cell viability, the down-regulation of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity, the reduction of apoptosis rate and pro-apoptotic protein (Bax) expression, and the increases of anti-apoptotic protein (Bcl-2) expression. In addition, kaempferol enhanced miR-21 level in H9c2 cells exposed to H/R, and inhibition of miR-21 induced by transfection with miR-21 inhibitor significantly blocked the protection of kaempferol against H/R-induced H9c2 cell injury. Furthermore, kaempferol eliminated H/R-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory response as illustrated by the decreases in reactive oxygen species generation and malondialdehyde content, the increases in antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activities, the decreases in pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-8 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels, and an increase in anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 level, while these effects of kaempferol were all reversed by miR-21 inhibitor. Moreover, results elicited that kaempferol remarkably blocks H/R-induced the down-regulation of Notch1 expression, the up-regulation of PTEN expression, and the reduction of P-Akt/Akt, indicating that kaempferol promotes Notch1/PTEN/AKT signaling pathway, and knockdown of Notch1/PTEN/AKT signaling pathway induced by Notch1 siRNA also abolished the protection of kaempferol against H/R-induced the damage of H9c2 cells. Notably, miR-21 inhibitor alleviated the promotion of kaempferol on Notch/PTEN/Akt signaling pathways in H9c2 cells exposed to H/R. Taken together, these above findings suggested thatmiR-21 mediates the protection of kaempferol against H/R-induced H9c2 cell injuryvia promoting Notch/PTEN/Akt signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

