RNase H-dependent PCR enables highly specific amplification of antibody variable domains from single B-cells
- PMID: 33152031
- PMCID: PMC7643965
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241803
RNase H-dependent PCR enables highly specific amplification of antibody variable domains from single B-cells
Abstract
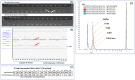
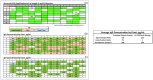
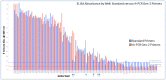
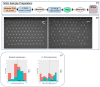
Immunization-based antibody discovery platforms require robust and effective protocols for the amplification, cloning, expression, and screening of antibodies from large numbers of B-cells in order to effectively capture the diversity of an experienced Ig-repertoire. Multiplex PCR using a series of forward and reverse primers designed to recover antibodies from a range of different germline sequences is challenging because primer design requires the recovery of full length antibody sequences, low starting template concentrations, and the need for all the primers to function under the same PCR conditions. Here we demonstrate several advantages to incorporating RNase H2-dependent PCR (rh-PCR) into a high-throughput, antibody-discovery platform. Firstly, rh-PCR eliminated primer dimer synthesis to below detectable levels, thereby eliminating clones with a false positive antibody titer. Secondly, by increasing the specificity of PCR, the rh-PCR primers increased the recovery of cognate antibody variable regions from single B-cells, as well as downstream recombinant antibody titers. Finally, we demonstrate that rh-PCR primers provide a more homogeneous sample pool and greater sequence quality in a Next Generation Sequencing-based approach to obtaining DNA sequence information from large numbers of cloned antibody cognate pairs. Furthermore, the higher specificity of the rh-PCR primers allowed for a better match between native antibody germline sequences and the VL/VH fragments amplified from single B-cells.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors have any commercial or other associations that might pose a conflict of interest with respect to this study. The employment of the authors by Eli Lilly & Company does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on data sharing and materials.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Systematic design and testing of nested (RT-)PCR primers for specific amplification of mouse rearranged/expressed immunoglobulin variable region genes from small number of B cells.J Immunol Methods. 2008 Dec 31;339(2):205-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2008.09.017. Epub 2008 Oct 14. J Immunol Methods. 2008. PMID: 18926828
-
IgG variable region and VH CDR3 diversity in unimmunized mice analyzed by massively parallel sequencing.Mol Immunol. 2014 Feb;57(2):274-83. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.09.008. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Mol Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24211535
-
Universal PCR amplification of mouse immunoglobulin gene variable regions: the design of degenerate primers and an assessment of the effect of DNA polymerase 3' to 5' exonuclease activity.J Immunol Methods. 2000 Jan 13;233(1-2):167-77. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(99)00184-2. J Immunol Methods. 2000. PMID: 10648866
-
Amplification of a minimally biased antibody repertoire for in vitro display using a universal primer-based amplification method.J Immunol Methods. 2021 Sep;496:113089. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2021.113089. Epub 2021 Jun 26. J Immunol Methods. 2021. PMID: 34181966
-
Primer Design and Inverse PCR on Yeast Display Antibody Selection Outputs.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1721:35-45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7546-4_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29423845 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-Invasive Characterization of the Pancreas During Bariatric Surgery via Circulating Pancreatic Specific Cell-free Messenger RNA.Front Genet. 2021 Oct 11;12:742496. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.742496. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34707641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moving up with the monoclonals [Internet]. BioPharma Dealmakers. https://biopharmadealmakers.nature.com/users/9880-biopharma-dealmakers/p...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

