Toxicodendron vernicifluum Stokes extract inhibits solid tumor growth and lung metastasis of 4T1 murine mammary carcinoma cells in BALB/c mice
- PMID: 33152052
- PMCID: PMC7646375
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241805
Toxicodendron vernicifluum Stokes extract inhibits solid tumor growth and lung metastasis of 4T1 murine mammary carcinoma cells in BALB/c mice
Abstract
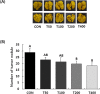
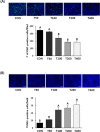
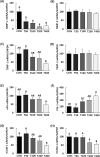
Toxicodendron vernicifluum Stokes has long been used as a food supplement and traditional herbal medicine in East Asia. We applied a new extraction method to produce Toxicodendron vernicifluum Stokes extract (TVSE), that doesn't contain urushiol (an allergenic toxin) but dose have higher levels of some flavonoids such as fustin and fisetin. This study was conducted to investigate the anticancer effects of TVSE in an in vivo system. Fifty BALB/c mice were acclimated for one week and then injected with 4T1 murine mammary carcinoma cells in mammary fat pads. After 7 days, the mice were randomly divided into 5 groups, and orally administered with 0, 50, 100, 200 or 400 mg of TVSE/kg body weight (BW)/day for 20 days. TVSE reduced tumor volume and weight dose-dependently. The expression of Ki67 was significantly reduced and the number of TUNEL-positive apoptotic cells was significantly increased in the TVSE-treated group over 100 mg/kg BW/day. While tumor nodules were not found in the liver, but only in lungs, the number of tumor nodules was reduced in a dose-dependent manner in the TVSE treated groups compared to the control group. In breast tumors, expression of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM-1) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was reduced by TVSE treatment. TVSE treatment significantly suppressed mRNA expression in tumors of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1, urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA), intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1, and vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1 while increasing plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI)-1. These results suggest that TVSE is potentially beneficial for the suppression of breast cancer growth and its-associated lung metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Medience Co. LTD. provided support in the form of salaries for authors KHK, SJP, but did not have any additional role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Oral administration of benzyl-isothiocyanate inhibits solid tumor growth and lung metastasis of 4T1 murine mammary carcinoma cells in BALB/c mice.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Nov;130(1):61-71. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-1299-8. Epub 2010 Dec 18. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 21170677
-
Dietary fat increases solid tumor growth and metastasis of 4T1 murine mammary carcinoma cells and mortality in obesity-resistant BALB/c mice.Breast Cancer Res. 2011 Aug 11;13(4):R78. doi: 10.1186/bcr2927. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21834963 Free PMC article.
-
Licochalcone E present in licorice suppresses lung metastasis in the 4T1 mammary orthotopic cancer model.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013 Jun;6(6):603-13. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-13-0012. Epub 2013 Apr 26. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013. PMID: 23625311
-
Oral administration of 3,3'-diindolylmethane inhibits lung metastasis of 4T1 murine mammary carcinoma cells in BALB/c mice.J Nutr. 2009 Dec;139(12):2373-9. doi: 10.3945/jn.109.111864. Epub 2009 Oct 28. J Nutr. 2009. PMID: 19864400
-
Traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Toxicodendron vernicifluum (Stokes) F.A. Barkley - A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 1;267:113476. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113476. Epub 2020 Oct 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33075438 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Anti-Metastatic Approaches of Herbal Medicines in 5 Major Cancers: From Traditional Medicine to Modern Drug Discovery.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Mar 27;10(4):527. doi: 10.3390/antiox10040527. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33801741 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

