Enzymatic synthesis of hypermodified DNA polymers for sequence-specific display of four different hydrophobic groups
- PMID: 33152081
- PMCID: PMC7708046
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa999
Enzymatic synthesis of hypermodified DNA polymers for sequence-specific display of four different hydrophobic groups
Abstract
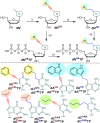
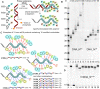
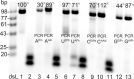
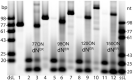
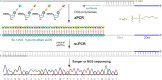
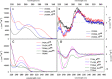
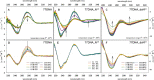
A set of modified 2'-deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs) bearing a linear or branched alkane, indole or phenyl group linked through ethynyl or alkyl spacer were synthesized and used as substrates for polymerase synthesis of hypermodified DNA by primer extension (PEX). Using the alkyl-linked dNTPs, the polymerase synthesized up to 22-mer fully modified oligonucleotide (ON), whereas using the ethynyl-linked dNTPs, the enzyme was able to synthesize even long sequences of >100 modified nucleotides in a row. In PCR, the combinations of all four modified dNTPs showed only linear amplification. Asymmetric PCR or PEX with separation or digestion of the template strand can be used for synthesis of hypermodified single-stranded ONs, which are monodispersed polymers displaying four different substituents on DNA backbone in sequence-specific manner. The fully modified ONs hybridized with complementary strands and modified DNA duplexes were found to exist in B-type conformation (B- or C-DNA) according to CD spectral analysis. The modified DNA can be replicated with high fidelity to natural DNA through PCR and sequenced. Therefore, this approach has a promising potential in generation and selection of hypermodified aptamers and other functional polymers.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Superanionic DNA: enzymatic synthesis of hypermodified DNA bearing four different anionic substituents at all four nucleobases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Nov 27;51(21):11428-11438. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad893. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37870471 Free PMC article.
-
Zwitterionic DNA: enzymatic synthesis of hypermodified DNA bearing four different cationic substituents at all four nucleobases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Feb 27;53(5):gkaf155. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf155. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40057376 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of acetylene linked double-nucleobase nucleos(t)ide building blocks and polymerase construction of DNA containing cytosines in the major groove.J Org Chem. 2011 May 6;76(9):3457-62. doi: 10.1021/jo200436j. Epub 2011 Mar 22. J Org Chem. 2011. PMID: 21425799
-
Synthesis of chemically modified DNA.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Jun 15;44(3):709-15. doi: 10.1042/BST20160051. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 27284032 Review.
-
Unnatural base pair systems for sensing and diagnostic applications.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2011 Apr;11(3):321-31. doi: 10.1586/erm.11.5. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2011. PMID: 21463241 Review.
Cited by
-
Expedient production of site specifically nucleobase-labelled or hypermodified RNA with engineered thermophilic DNA polymerases.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 9;15(1):3054. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47444-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38594306 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid-linked nucleoside triphosphates for enzymatic synthesis of hydrophobic oligonucleotides with enhanced membrane anchoring efficiency.Chem Sci. 2023 Mar 20;14(15):4059-4069. doi: 10.1039/d2sc06718h. eCollection 2023 Apr 12. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 37063801 Free PMC article.
-
Polymerase Synthesis of Hypermodified DNA Displaying a Combination of Thiol, Hydroxyl, Carboxylate, and Imidazole Functional Groups in the Major Groove.Chemistry. 2025 Jun 17;31(34):e202501034. doi: 10.1002/chem.202501034. Epub 2025 May 15. Chemistry. 2025. PMID: 40327399 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Covalent Interactions between dUTP C5-Substituents and DNA Polymerase Decrease PCR Efficiency.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 4;24(17):13643. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713643. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686447 Free PMC article.
-
Dependence of click-SELEX performance on the nature and average number of modified nucleotides.RSC Chem Biol. 2022 Feb 21;3(3):288-294. doi: 10.1039/d2cb00012a. eCollection 2022 Mar 9. RSC Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 35359492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dunn M.R., Jimenez R.M., Chaput J.C.. Analysis of aptamer discovery and technology. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017; 1:0076.
-
- Ng E.W.M., Shima D.T., Calias P., Cunningham E.T., Guyer D.R., Adamis A.P.. Pegaptanib, a targeted anti-VEGF aptamer for ocular vascular disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006; 5:123–132. - PubMed
-
- Ma H., Liu J., Ali M.M., Mahmood M.A.I., Labanieh L., Lu M., Iqbal S.M., Zhang Q., Zhao W., Wan Y.C.. Nucleic acid aptamers in cancer research, diagnostics and therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015; 44:1240–1256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

