Implicating ILK in inflammation
- PMID: 33152089
- PMCID: PMC7645982
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2020008316
Implicating ILK in inflammation
Abstract
In this issue of Blood,
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
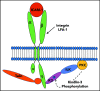
Comment on
-
The integrin-linked kinase is required for chemokine-triggered high-affinity conformation of the neutrophil β2-integrin LFA-1.Blood. 2020 Nov 5;136(19):2200-2205. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020004948. Blood. 2020. PMID: 32730588
References
-
- Margraf A, Germena G, Drexler HCA, et al. . The integrin-linked kinase is required for chemokine-triggered high-affinity conformation of the neutrophil β2-integrin LFA1. Blood. 2020;136(19):2200-2205. - PubMed
-
- Hannigan GE, Leung-Hagesteijn C, Fitz-Gibbon L, et al. . Regulation of cell adhesion and anchorage-dependent growth by a new beta 1-integrin-linked protein kinase. Nature. 1996;379(6560):91-96. - PubMed
-
- Legate KR, Montañez E, Kudlacek O, Fässler R. ILK, PINCH and parvin: the tIPP of integrin signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(1):20-31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

