Bibliometric evaluation of Latin American contributions on COVID-19
- PMID: 33152194
- PMCID: PMC7676830
- DOI: 10.7705/biomedica.5571
Bibliometric evaluation of Latin American contributions on COVID-19
Abstract
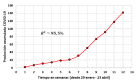
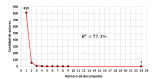
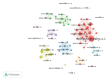
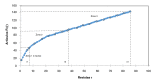
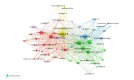
Introduction: The propagation of COVID-19, an infectious disease caused by the novel SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, has become a pandemic which, along with its rapid dissemination worldwide, has brought about an exponential increase in the amount of research related to the subject to which Latin American researchers have contributed actively. Objective: To conduct a descriptive bibliometric study of the main trends in research on COVID-19 produced in Latin America. Materials and methods: We searched in the Web of Science, Scopus, and Pubmed databases to retrieve the Latin American scientific production on COVID-19. Bibliometric indicators of production, visibility, impact, and collaboration were analyzed to assess the regional participation in studies on the subject. Results: The analysis of 142 documents evidenced an exponential growth of scientific production in the period analyzed, an important level of international collaboration (51.4%) in scientific production, and the leadership of regional institutions (71%) in the research with publications in high-visibility jounals especially in Colombia, Brazil, and México. Conclusions: The results regarding the regional participation in the research on COVID-19 were relevant not only in relation to its quantity and exponential growth during the period analyzed but also in terms of its quality and excellence with a high rate of international collaboration and publications in important scientific journals, which besides their visibility, represent a considerable contribution to the research compared to the other geographical contexts.
Introducción. La propagación de la COVID-19, una enfermedad infecciosa causada por el nuevo coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, se ha convertido en una pandemia que, a la par de su rápida diseminación a nivel mundial, ha traído consigo un aumento exponencial de la cantidad de estudios relacionados con el tema, fenómeno en el que los investigadores de Latinoamérica han participado activamente. Objetivo. Llevar a cabo un estudio bibliométrico descriptivo para identificar las tendencias de la investigación sobre COVID-19 producida en Latinoamérica. Materiales y métodos. Se recurrió a las bases de datos Web of Science, Scopus y Pubmed para recuperar la producción científica latinoamericana sobre COVID-19. Se analizaron los indicadores bibliométricos de producción, visibilidad, impacto y colaboración para evaluar la participación regional en la investigación sobre el tema. Resultados. El análisis de 142 documentos evidenció un crecimiento exponencial de la producción científica en el corto periodo analizado, una significativa colaboración internacional (51,4 %), y el liderazgo de las instituciones regionales (71 %) en la investigación con aportes en revistas de alta visibilidad, especialmente de Colombia, Brasil y México. Conclusiones. El estudio evidenció resultados relevantes sobre la participación regional en la investigación sobre COVID-19, no solo en cuanto a la cantidad y el crecimiento exponencial, sino también a su calidad y excelencia, con una elevada tasa de colaboración internacional y de publicación en revistas de reconocido prestigio, lo que, además de ser clave para la visibilidad de los países, es un considerable aporte a las investigaciones que se realizan en otros contextos geográficos.
Keywords: Coronavirus infections; bibliometrics; bibliometric indicators; information management; Latin America.
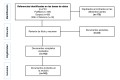
Figures
Comment in
-
Bibliometric evaluation of Latin American contributions on COVID-19.Biomedica. 2020 Oct 30;40(Supl. 2):205-208. Biomedica. 2020. PMID: 33152205 Free PMC article. English, Spanish. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Bibliometric evaluation of Latin American contributions on COVID-19.Biomedica. 2020 Oct 30;40(Supl. 2):205-208. Biomedica. 2020. PMID: 33152205 Free PMC article. English, Spanish. No abstract available.
-
Research Progress of Coronavirus Based on Bibliometric Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 May 26;17(11):3766. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17113766. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32466477 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): A Machine Learning Bibliometric Analysis.In Vivo. 2020 Jun;34(3 Suppl):1613-1617. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11951. In Vivo. 2020. PMID: 32503819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Journal of Optometry in Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI) and peer-review process during COVID-19 pandemic.J Optom. 2020 Oct-Dec;13(4):213-215. doi: 10.1016/j.optom.2020.06.003. J Optom. 2020. PMID: 32988579 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
[COVID-19 in Latin America: a systematic review and bibliometric analysis].Rev Salud Publica (Bogota). 2020 Mar 1;22(2):246-252. doi: 10.15446/rsap.V22n2.86878. Rev Salud Publica (Bogota). 2020. PMID: 36753116 Spanish.
Cited by
-
Latin American Scientific Production on COVID-19 Vaccines.Ethiop J Health Sci. 2022 Mar;32(2):235-242. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v32i2.3. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2022. PMID: 35693566 Free PMC article.
-
The promising drugs included in WHO's Solidarity Project: a choice based in scientific knowledge and institutional competencies.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2021 Sep 1;116:e200603. doi: 10.1590/0074-02760200603. eCollection 2021. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2021. PMID: 34495083 Free PMC article.
-
[Mapping of research protocols, publications, and collaborations on COVID-19 in Latin America and the CaribbeanMapeamento de protocolos de pesquisa, publicações e colaborações sobre COVID-19 na América Latina e no Caribe].Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2022 May 2;46:e42. doi: 10.26633/RPSP.2022.42. eCollection 2022. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2022. PMID: 35520021 Free PMC article. Spanish.
-
Bibliometric evaluation of Latin American contributions on COVID-19.Biomedica. 2020 Oct 30;40(Supl. 2):205-208. Biomedica. 2020. PMID: 33152205 Free PMC article. English, Spanish. No abstract available.
-
Description and Analysis of Research on Death and Dying during the COVID-19 Pandemic, Published in Nursing Journals Indexed in SCOPUS.Nurs Rep. 2024 Mar 22;14(2):655-674. doi: 10.3390/nursrep14020050. Nurs Rep. 2024. PMID: 38525696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - March 3. 2020. [20 de abril de 2020]. Disponible en: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re....
-
- Rodríguez-Morales AJ, Sánchez-Duque JA, Botero SH, Pérez-Díaz CE, Villamil-Gómez WE, Méndez CA, et al. Preparación y control de la enfermedad por coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) en América Latina. Acta Med Perú. 2020;37:3–7.
-
- Torres-Salinas D. Ritmo de crecimiento diario de la producción científica sobre Covid-19. Análisis en bases de datos y repositorios en acceso abierto. El Profesional de la Información. 2020;29:e290215. doi: 10.3145/epi.2020.mar.15. - DOI
-
- Alba-Ruiz R. Covid-19, coronavirus pandemic: aproximación bibliométrica y revisión de los resultados. Zenodo. 2020 doi: 10.5281/zenodo.3734062. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous