Investigation of the efficacy of mycotoxin-detoxifying additive on health and growth of newly-weaned pigs under deoxynivalenol challenges
- PMID: 33152208
- PMCID: PMC7961193
- DOI: 10.5713/ajas.20.0567
Investigation of the efficacy of mycotoxin-detoxifying additive on health and growth of newly-weaned pigs under deoxynivalenol challenges
Abstract
Objective: This study evaluated the effects of feeding diets naturally contaminated with deoxynivalenol (supplemental 2 mg/kg) on health, growth, and the effects of a mycotoxindetoxifying additive in newly-weaned pigs.
Methods: Thirty-six pigs (27 day-old) were housed individually and assigned to 3 treatments for 5 weeks: CON (diet containing minimal deoxynivalenol), MT (diet with supplemental 1.9 mg/kg of deoxynivalenol), and MT+D (MT + mycotoxin-detoxifying additive, 0.2%, MegaFix, ICC, São Paulo, Brazil). The mycotoxin-detoxifying additive included bentonite, algae, enzymes, and yeast. Blood was taken at week 2 and 5. Jejunal tissue were taken at week 5. Data were analyzed using the MIXED procedure of SAS.
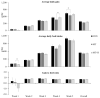
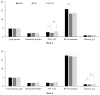
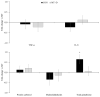
Results: Pigs fed MT+D tended to have decreased (p = 0.056) averaged daily feed intake during week 1 than MT. At week 2, serum aspartate aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase in MT tended to be lower (p = 0.059) than CON, whereas it was increased (p< 0.05) for MT+D than MT, indicating hepatic damages in MT and recovery in MT+D. Pigs fed MT had lower (p<0.05) blood urea nitrogen/creatinine than CON, supporting hepatic damage. At week 5, pigs fed MT tended to have reduced (p = 0.079) glucose than CON, whereas it was increased (p<0.05) for MT+D than MT, indicating impaired intestinal glucose absorption in MT, which was improved in MT+D. Pigs fed CON tended to have increased (p = 0.057) total glutathione in jejunum than MT, indicating oxidative stress in MT. Pigs fed MT+D had a reduced (p<0.05) proportion of Ki-67-positive cells in jejunum than MT, indicating lower enterocyte proliferation in MT+D.
Conclusion: Feeding supplemental 1.9 mg/kg of deoxynivalenol reduced growth and debilitated hepatic health of pigs, as seen in leakage of hepatic enzymes, impaired nitrogen metabolism, and increase in oxidative stress. The mycotoxin-detoxifying enhanced hepatic health and glucose levels, and attenuated gut damage in pigs fed deoxynivalenol contaminated diets.
Keywords: Adsorbent; Deoxynivalenol; Enzyme; Gut Health; Pig; Probiotic.
Conflict of interest statement
We certify that there is no conflict of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Mycotoxin-Sequestering Agents on Growth Performance and Nutrient Utilization of Growing Pigs Fed Deoxynivalenol-Contaminated Diets.Life (Basel). 2023 Sep 23;13(10):1953. doi: 10.3390/life13101953. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895335 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Mycotoxin Detoxifiers on Health and Growth of Newly-Weaned Pigs under Chronic Dietary Challenge of Deoxynivalenol.Toxins (Basel). 2020 May 9;12(5):311. doi: 10.3390/toxins12050311. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32397551 Free PMC article.
-
Phytobiotics with Adsorbent to Mitigate Toxicity of Multiple Mycotoxins on Health and Growth of Pigs.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jun 26;13(7):442. doi: 10.3390/toxins13070442. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34206784 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the Efficacy of a Postbiotic Yeast Cell Wall-Based Blend on Newly-Weaned Pigs under a Dietary Challenge of Multiple Mycotoxins with Emphasis on Deoxynivalenol.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Aug 6;12(8):504. doi: 10.3390/toxins12080504. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32781569 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of two yeast based feed additives on pigs chronically exposed to deoxynivalenol and zearalenone.Toxins (Basel). 2014 Dec 12;6(12):3336-53. doi: 10.3390/toxins6123336. Toxins (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25533517 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of Mycotoxin-Sequestering Agents on Growth Performance and Nutrient Utilization of Growing Pigs Fed Deoxynivalenol-Contaminated Diets.Life (Basel). 2023 Sep 23;13(10):1953. doi: 10.3390/life13101953. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895335 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal Damages by F18+Escherichia coli and Its Amelioration with an Antibacterial Bacitracin Fed to Nursery Pigs.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 May 3;12(5):1040. doi: 10.3390/antiox12051040. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237906 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of non-starch polysaccharide sources with enzymes influencing intestinal mucosa-associated microbiota and mucosal immunity of nursery pigs on growth and carcass traits at market weight.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025 Apr 1;16(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s40104-025-01170-4. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40165296 Free PMC article.
-
The administration of diets contaminated with low to intermediate doses of deoxynivalenol and supplemented with antioxidants and binding agents slightly affects the growth, antioxidant status, and vaccine response in weanling pigs.J Anim Sci. 2021 Sep 1;99(9):skab238. doi: 10.1093/jas/skab238. J Anim Sci. 2021. PMID: 34406414 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of β-mannanase on intestinal health and growth performance of nursery to growing pigs fed diets with DDGS.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf238. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf238. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40734338 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

