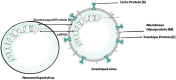
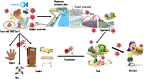
SARS-CoV-2 in hospital wastewater during outbreak of COVID-19: A review on detection, survival and disinfection technologies
- PMID: 33153744
- PMCID: PMC7585361
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143192
SARS-CoV-2 in hospital wastewater during outbreak of COVID-19: A review on detection, survival and disinfection technologies
Abstract
Currently, the apparition of new SARS-CoV, known as SARS-CoV-2, affected more than 34 million people and causing high death rates worldwide. Recently, several studies reported SARS-CoV-2 ribonucleic acid (RNA) in hospital wastewater. SARS-CoV-2 can be transmitted between humans via respiratory droplets, close contact and fomites. Fecal-oral transmission is considered also as a potential route of transmission since several scientists confirmed the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in feces of infected patients, therefore its transmission via feces in aquatic environment, particularly hospital wastewater. Hospitals are one of the important classes of polluting sectors around the world. It was identified that hospital wastewater contains hazardous elements and a wide variety of microbial pathogens and viruses. Therefore, this may potentially pose a significant risk of public health and environment infection. This study reported an introduction about the Physical-chemical and microbiological characterization of hospital wastewater, which can be a route to identify potential technology to reduce the impact of hospital contaminants before evacuation. The presence of SARS-CoV-2 in aqueous environment was reviewed. The knowledge of the detection and survival of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater and hospital wastewater were described to understand the different routes of SARS-CoV-2 transmission, which is also useful to avoid the outbreak of CoV-19. In addition, disinfection technologies used commonly for deactivation of SARS-CoV-2 were highlighted. It was revealed that, chlorine-containing disinfectants are the most commonly used disinfectants in this field of research. Meanwhile, other efficient technologies must be developed and improved to avoid another wave of the pandemic of COVID-19 infections.
Keywords: Detection; Disinfection technologies; Hospital wastewater; SARS-CoV-2; Survival; Transmission.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed W., Angel N., Edson J., Bibby K., Bivins A., Brien J.W.O.…Mueller J.F. First confirmed detection of SARSCoV- 2 in untreated wastewater in Australia: a proof of concept for the wastewater surveillance of COVID-19 in the community. Science of the Total Environment. 2020;728:138764. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al Aukidy M., Al Chalabi S., Verlicchi P. Hospital wastewater treatments adopted in Asia, Africa, and Australia. Hospital Wastewaters. 2018;60:171–188.
-
- Arbely E., Granot Z., Kass I., Orly J., Arkin I.T.A. Trimerizing GxxxG motif is uniquely inserted in the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus spike protein transmembrane domain. Biochemistry. 2006;45:11349–11356. - PubMed
-
- Basturka I., Varankb G., Murat-Hocaoglua S., Yazici-Guvenc S., Oktem-Olguna E.E., Canli O. Characterization and treatment of medical laboratory wastewater by ozonation: optimization of toxicity removal by central composite design. The Journal of the International Ozone Association: Ozone: Science & Engineering. 2020 doi: 10.1080/01919512.2020.1794794. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous