An ultrapotent synthetic nanobody neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 by stabilizing inactive Spike
- PMID: 33154106
- PMCID: PMC7857409
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abe3255
An ultrapotent synthetic nanobody neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 by stabilizing inactive Spike
Abstract
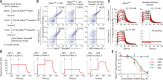
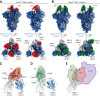
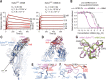
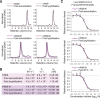
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus enters host cells via an interaction between its Spike protein and the host cell receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). By screening a yeast surface-displayed library of synthetic nanobody sequences, we developed nanobodies that disrupt the interaction between Spike and ACE2. Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) revealed that one nanobody, Nb6, binds Spike in a fully inactive conformation with its receptor binding domains locked into their inaccessible down state, incapable of binding ACE2. Affinity maturation and structure-guided design of multivalency yielded a trivalent nanobody, mNb6-tri, with femtomolar affinity for Spike and picomolar neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 infection. mNb6-tri retains function after aerosolization, lyophilization, and heat treatment, which enables aerosol-mediated delivery of this potent neutralizer directly to the airway epithelia.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures

Update of
-
An ultra-potent synthetic nanobody neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 by locking Spike into an inactive conformation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Aug 17:2020.08.08.238469. doi: 10.1101/2020.08.08.238469. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Science. 2020 Dec 18;370(6523):1473-1479. doi: 10.1126/science.abe3255. PMID: 32817938 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Ksiazek T. G., Erdman D., Goldsmith C. S., Zaki S. R., Peret T., Emery S., Tong S., Urbani C., Comer J. A., Lim W., Rollin P. E., Dowell S. F., Ling A.-E., Humphrey C. D., Shieh W.-J., Guarner J., Paddock C. D., Rota P., Fields B., DeRisi J., Yang J.-Y., Cox N., Hughes J. M., LeDuc J. W., Bellini W. J., Anderson L. J., SARS Working Group , A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 1953–1966 (2003). 10.1056/NEJMoa030781 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhou P., Yang X.-L., Wang X.-G., Hu B., Zhang L., Zhang W., Si H.-R., Zhu Y., Li B., Huang C.-L., Chen H.-D., Chen J., Luo Y., Guo H., Jiang R.-D., Liu M.-Q., Chen Y., Shen X.-R., Wang X., Zheng X.-S., Zhao K., Chen Q.-J., Deng F., Liu L.-L., Yan B., Zhan F.-X., Wang Y.-Y., Xiao G.-F., Shi Z.-L., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 579, 270–273 (2020). 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan J. F., Yuan S., Kok K.-H., To K. K.-W., Chu H., Yang J., Xing F., Liu J., Yip C. C.-Y., Poon R. W.-S., Tsoi H.-W., Lo S. K.-F., Chan K.-H., Poon V. K.-M., Chan W.-M., Ip J. D., Cai J.-P., Cheng V. C.-C., Chen H., Hui C. K.-M., Yuen K.-Y., A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: A study of a family cluster. Lancet 395, 514–523 (2020). 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang C., Wang Y., Li X., Ren L., Zhao J., Hu Y., Zhang L., Fan G., Xu J., Gu X., Cheng Z., Yu T., Xia J., Wei Y., Wu W., Xie X., Yin W., Li H., Liu M., Xiao Y., Gao H., Guo L., Xie J., Wang G., Jiang R., Gao Z., Jin Q., Wang J., Cao B., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 395, 497–506 (2020). 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S10 OD021741/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM125217/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI142733/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201400008C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008284/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP5 OD023048/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- F31 NS113432/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM126218/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM124149/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 GM138753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- U19 AI135990/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM137463/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 EB009383/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD020054/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

