Epidemiology and transmission dynamics of COVID-19 in two Indian states
- PMID: 33154136
- PMCID: PMC7857399
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abd7672
Epidemiology and transmission dynamics of COVID-19 in two Indian states
Abstract
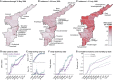
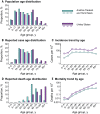
Although most cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) have occurred in low-resource countries, little is known about the epidemiology of the disease in such contexts. Data from the Indian states of Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh provide a detailed view into severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) transmission pathways and mortality in a high-incidence setting. Reported cases and deaths have been concentrated in younger cohorts than would be expected from observations in higher-income countries, even after accounting for demographic differences across settings. Among 575,071 individuals exposed to 84,965 confirmed cases, infection probabilities ranged from 4.7 to 10.7% for low-risk and high-risk contact types, respectively. Same-age contacts were associated with the greatest infection risk. Case fatality ratios spanned 0.05% at ages of 5 to 17 years to 16.6% at ages of 85 years or more. Primary data from low-resource countries are urgently needed to guide control measures.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures


Comment in
-
Public health during the pandemic in India.Science. 2020 Nov 6;370(6517):663-664. doi: 10.1126/science.abe9707. Science. 2020. PMID: 33154127 No abstract available.
References
-
- Li Q., Guan X., Wu P., Wang X., Zhou L., Tong Y., Ren R., Leung K. S. M., Lau E. H. Y., Wong J. Y., Xing X., Xiang N., Wu Y., Li C., Chen Q., Li D., Liu T., Zhao J., Liu M., Tu W., Chen C., Jin L., Yang R., Wang Q., Zhou S., Wang R., Liu H., Luo Y., Liu Y., Shao G., Li H., Tao Z., Yang Y., Deng Z., Liu B., Ma Z., Zhang Y., Shi G., Lam T. T. Y., Wu J. T., Gao G. F., Cowling B. J., Yang B., Leung G. M., Feng Z., Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 1199–1207 (2020). 10.1056/NEJMoa2001316 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou F., Yu T., Du R., Fan G., Liu Y., Liu Z., Xiang J., Wang Y., Song B., Gu X., Guan L., Wei Y., Li H., Wu X., Xu J., Tu S., Zhang Y., Chen H., Cao B., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 395, 1054–1062 (2020). 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guan W. J., Ni Z. Y., Hu Y., Liang W. H., Ou C. Q., He J. X., Liu L., Shan H., Lei C. L., Hui D. S. C., Du B., Li L. J., Zeng G., Yuen K.-Y., Chen R. C., Tang C. L., Wang T., Chen P. Y., Xiang J., Li S. Y., Wang J. L., Liang Z. J., Peng Y. X., Wei L., Liu Y., Hu Y. H., Peng P., Wang J. M., Liu J. Y., Chen Z., Li G., Zheng Z. J., Qiu S. Q., Luo J., Ye C. J., Zhu S. Y., Zhong N. S., Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 1708–1720 (2020). 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grasselli G., Zangrillo A., Zanella A., Antonelli M., Cabrini L., Castelli A., Cereda D., Coluccello A., Foti G., Fumagalli R., Iotti G., Latronico N., Lorini L., Merler S., Natalini G., Piatti A., Ranieri M. V., Scandroglio A. M., Storti E., Cecconi M., Pesenti A., Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy region, Italy. JAMA 323, 1574–1581 (2020). 10.1001/jama.2020.5394 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Docherty A. B., Harrison E. M., Green C. A., Hardwick H. E., Pius R., Norman L., Holden K. A., Read J. M., Dondelinger F., Carson G., Merson L., Lee J., Plotkin D., Sigfrid L., Halpin S., Jackson C., Gamble C., Horby P. W., Nguyen-Van-Tam J. S., Ho A., Russell C. D., Dunning J., Openshaw P. J. M., Baillie J. K., Semple M. G., Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: Prospective observational cohort study. BMJ 369, m1985 (2020). 10.1136/bmj.m1985 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

