HDL cholesterol efflux capacity is inversely associated with subclinical cardiovascular risk markers in young adults: The cardiovascular risk in Young Finns study
- PMID: 33154477
- PMCID: PMC7645719
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-76146-7
HDL cholesterol efflux capacity is inversely associated with subclinical cardiovascular risk markers in young adults: The cardiovascular risk in Young Finns study
Abstract
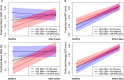
The atherogenic process begins already in childhood and progresses to symptomatic condition with age. We investigated the association of cholesterol efflux capacity (CEC) and vascular markers of subclinical atherosclerosis in healthy, young adults. CEC was determined in 2282 participants of the Young Finns study using cAMP treated 3H-cholesterol-labeled J774 cells. The CEC was correlated to baseline and 6-year follow-up data of cardiovascular risk factors and ultrasound measurements of arterial structure and function. CEC was higher in women, correlated with total cholesterol, HDL-C, and apolipoprotein A-I, but not with LDL-C or apolipoprotein B. Compared to the lowest CEC quartile, the highest CEC quartile was significantly associated with high CRP levels and inversely associated with adiponectin. At baseline, high CEC was associated with decreased flow-mediated dilation (FMD) and carotid artery distensibility, as well as an increased Young's modulus of elasticity, indicating adverse changes in arterial structure, and function. The association reversed with follow-up FMD data, indicating the interaction of preclinical parameters over time. A higher CEC was directly associated with a lower risk of subclinical atherosclerosis at follow-up. In young and healthy subjects, CEC was associated with important lipid risk parameters at baseline, as in older patients and CAD patients, but inversely with early risk markers for subclinical atherosclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Anastasius M, Luquain-Costaz C, Kockx M, Jessup W, Kritharides L. A critical appraisal of the measurement of serum 'cholesterol efflux capacity' and its use as surrogate marker of risk of cardiovascular disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids. 1863;1257–1273:2018. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.08.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

