A Comparative Study on the Strategies Adopted by the United Kingdom, India, China, Italy, and Saudi Arabia to Contain the Spread of the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 33154693
- PMCID: PMC7608628
- DOI: 10.2147/JHL.S266491
A Comparative Study on the Strategies Adopted by the United Kingdom, India, China, Italy, and Saudi Arabia to Contain the Spread of the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
Purpose: The objective of this study was to compare the strategies adopted by the United Kingdom, Italy, China, India, and Saudi Arabia to contain the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Materials and methods: A review of the literature was carried out to collect data on the strategies used by China, Italy, India, the United Kingdom, and Saudi Arabia to contain the spread of the COVID-19 virus. The global analysis of 65 published literature references allowed observing the effectiveness and efficiency of the strategies used by these countries to control the spread of the COVID-19 virus.
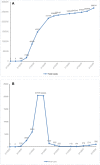
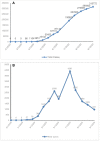
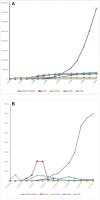
Results: Both mitigation and suppression strategies were adopted by the United Kingdom, India, Italy, China, and Saudi Arabia to control the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic. It was observed that China has achieved a greater success in flattening the curve compared to the other countries. In China, few new daily cases have occurred since March, and it has been the only country that has managed to keep the COVID-19 pandemic under control. On the other hand, reductions in the number of daily cases (since May 2020) were detected in the United Kingdom, Italy, and Saudi Arabia (since July 2020). Also, during the last 3 months (June, July and August) India has shown the highest growth in the total number of confirmed cases and in the number of new daily cases, compared to the mentioned countries.
Conclusion: The review of the strategies adopted by China, India, the United Kingdom, Italy and Saudi Arabia to combat the COVID-19 pandemic can guide countries in the design and development of mitigation and suppression approaches to control the spread of the COVID-19 virus. Containment strategies such as lockdowns cannot continue in the long term. Therefore, countries must adopt mitigation and prevention strategies to protect people from infection and learn to live with the virus.
Keywords: COVID-19 outbreak; lockdown strategy; mitigation and suppression strategies; novel coronavirus; pandemic.
© 2020 Alanezi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Mayo Clinic. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Available from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/coronavirus/symptoms-caus.... Accessed June1, 2020.
-
- World Health Organization. WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed June1, 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

