A real-life correlation between clinical SYNTAX score II and carotid intima-media thickness in patients with stable coronary artery disease
- PMID: 33154885
- PMCID: PMC7640613
- DOI: 10.37616/2212-5043.1002
A real-life correlation between clinical SYNTAX score II and carotid intima-media thickness in patients with stable coronary artery disease
Abstract
Background: SYNTAX score II (SSII) is an update of the established SYNTAX score (SS) that uses clinical variables such as age, sex, creatinine clearance, left ventricular ejection fraction, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and peripheral arterial disease. Furthermore, SSII has been proven to be a more powerful predictive tool than SS in patients with complex coronary artery disease (CAD). Carotid õntima-media thickness (CIMT) is a widely used noninvasive evidence for subclinical or early atherosclerosis, and it was proved to be an independent predictor for cardiovascular events. Most of the previously published articles studied the association between the CIMT with old cardiovascular scoring systems such as SSI and Gensini score with debatable data about their correlation.
Aim: To study the correlation between SSII and CIMT in stable CAD patients undergoing elective coronary angiography (CA).
Method and patients: A prospective study including 155 patients undergoing elective CA for stable CAD excluding patients with history of acute coronary syndrome, previous coronary revascularization either by percutaneous coronary intervention or coronary artery bypass grafting, and previous cerebrovascular stroke.
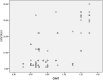
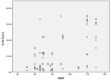
Results: The mean age of patients was 58.25 ± 16.46 years, and 79 patients (50.96%) were men. The mean SSII score was 10.23 ± 11.36 and mean CIMT was 0.85 ± 0.24. The correlation between SSII and CIMT using Spearman correlation showed a strong correlation between SSII score and CIMT with correlation coefficient r = 0.752.
Conclusion: The study showed a strong positive correlation between SSII and CIMT in stable CAD patients undergoing elective CA.
Keywords: Cardiovascular events; Carotid artery; Carotid intima-media thickness; Coronary angiogram; Coronary artery disease; Correlation; SYNTAX score II; Ultrasound.
© 2020 Saudi Heart Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Saito D, Shiraki T, Oka T, Kajiyama A, Doi M, Masaka T. Morphologic correlation between atherosclerotic lesions of the carotid and coronary arteries in patients with angina pectoris. Jpn Circ J. 1999;63:522–6. - PubMed
-
- Ikeda N, Kogame N, Iijima R, Nakamura M, Sugi K. Carotid artery intima-media thickness and plaque score can predict the SYNTAX score. Eur Heart J. 2011;33:113–9. - PubMed
-
- Costanzo L, Campisano M, Capodanno D, Sole A, Grasso C, Ragusa M, et al. The SYNTAX score does not predict presence of carotid disease in a multivessel coronary disease population. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;83:1169–75. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
