Unpacking the implementation blackbox using 'actor interface analysis': how did actor relations and practices of power influence delivery of a free entitlement health policy in India?
- PMID: 33156935
- PMCID: PMC7646725
- DOI: 10.1093/heapol/czaa125
Unpacking the implementation blackbox using 'actor interface analysis': how did actor relations and practices of power influence delivery of a free entitlement health policy in India?
Abstract
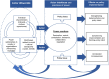
Exploring the implementation blackbox from a perspective that considers embedded practices of power is critical to understand the policy process. However, the literature is scarce on this subject. To address the paucity of explicit analyses of everyday politics and power in health policy implementation, this article presents the experience of implementing a flagship health policy in India. Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram (JSSK), launched in the year 2011, has not been able to fully deliver its promises of providing free maternal and child health services in public hospitals. To examine how power practices, influence implementation, we undertook a qualitative analysis of JSSK implementation in one state of India. We drew on an actor-oriented perspective of development and used 'actor interface analysis' to guide the study design and analysis. Data collection included in-depth interviews of implementing actors and JSSK service recipients, document review and observations of actor interactions. A framework analysis method was used for analysing data, and the framework used was founded on the constructs of actor lifeworlds, which help understand the often neglected and lived realities of policy actors. The findings illustrate that implementation was both strengthened and constrained by practices of power at various interface encounters. The implementation decisions and actions were influenced by power struggles such as domination, control, resistance, contestation, facilitation and collaboration. Such practices were rooted in: Social and organizational power relationships like organizational hierarchies and social positions; personal concerns or characteristics like interests, attitudes and previous experiences and the worldviews of actors constructed by social and ideological paradigms like their values and beliefs. Application of 'actor interface analysis' and further nuancing of the concept of 'actor lifeworlds' to understand the origin of practices of power can be useful for understanding the influence of everyday power and politics on the policy process.
Keywords: Health policy; framework; health services research; health systems research; implementation; policy analysis; policy implementation; policy process; power; qualitative research.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press in association with The London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Asian Productivity Organization T. 2003. Rural Life Improvement in Asia. In: Cruz D.A. (ed), 47–64. Tokyo.
-
- Barrett S and Fudge C(eds). 1981. Policy and action: essays on the implementation of public policy. Abingdon: Routledge.