Phosphatase of Regenerating Liver-1 Selectively Times Circadian Behavior in Darkness via Function in PDF Neurons and Dephosphorylation of TIMELESS
- PMID: 33157022
- PMCID: PMC7855481
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.10.013
Phosphatase of Regenerating Liver-1 Selectively Times Circadian Behavior in Darkness via Function in PDF Neurons and Dephosphorylation of TIMELESS
Abstract
The timing of behavior under natural light-dark conditions is a function of circadian clocks and photic input pathways, but a mechanistic understanding of how these pathways collaborate in animals is lacking. Here we demonstrate in Drosophila that the Phosphatase of Regenerating Liver-1 (PRL-1) sets period length and behavioral phase gated by photic signals. PRL-1 knockdown in PDF clock neurons dramatically lengthens circadian period. PRL-1 mutants exhibit allele-specific interactions with the light- and clock-regulated gene timeless (tim). Moreover, we show that PRL-1 promotes TIM accumulation and dephosphorylation. Interestingly, the PRL-1 mutant period lengthening is suppressed in constant light, and PRL-1 mutants display a delayed phase under short, but not long, photoperiod conditions. Thus, our studies reveal that PRL-1-dependent dephosphorylation of TIM is a core mechanism of the clock that sets period length and phase in darkness, enabling the behavioral adjustment to change day-night cycles.
Keywords: Drosophila; circadian; phosphorylation; photoperiod; seasonality.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


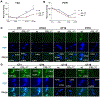

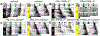
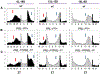

References
-
- Curtin KD, Huang ZJ, and Rosbash M (1995). Temporally regulated nuclear entry of the Drosophila period protein contributes to the circadian clock. Neuron 14, 365–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

