β-Coronaviruses Use Lysosomes for Egress Instead of the Biosynthetic Secretory Pathway
- PMID: 33157038
- PMCID: PMC7590812
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.039
β-Coronaviruses Use Lysosomes for Egress Instead of the Biosynthetic Secretory Pathway
Abstract
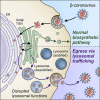
β-Coronaviruses are a family of positive-strand enveloped RNA viruses that includes the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Much is known regarding their cellular entry and replication pathways, but their mode of egress remains uncertain. Using imaging methodologies and virus-specific reporters, we demonstrate that β-coronaviruses utilize lysosomal trafficking for egress rather than the biosynthetic secretory pathway more commonly used by other enveloped viruses. This unconventional egress is regulated by the Arf-like small GTPase Arl8b and can be blocked by the Rab7 GTPase competitive inhibitor CID1067700. Such non-lytic release of β-coronaviruses results in lysosome deacidification, inactivation of lysosomal degradation enzymes, and disruption of antigen presentation pathways. β-Coronavirus-induced exploitation of lysosomal organelles for egress provides insights into the cellular and immunological abnormalities observed in patients and suggests new therapeutic modalities.
Keywords: CD1067700; Rab7; SARS-CoV-2; acidification/deacidification ARL8b; antigen presentation; coronavirus; lysosome; pH; viral egress; viral immunology.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
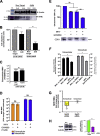
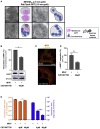
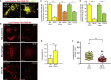
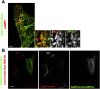
Comment in
-
Actively or passively deacidified lysosomes push β-coronavirus egress.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Mar 4;12(3):235. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03501-5. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33664221 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Aranda-Romo S., Garcia-Sepulveda C.A., Comas-García A., Lovato-Salas F., Salgado-Bustamante M., Gómez-Gómez A., Noyola D.E. Killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR) in severe A (H1N1) 2009 influenza infections. Immunogenetics. 2012;64:653–662. - PubMed
-
- Ballabio A., Bonifacino J.S. Lysosomes as dynamic regulators of cell and organismal homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020;21:101–118. - PubMed
-
- Boda A., Lőrincz P., Takáts S., Csizmadia T., Tóth S., Kovács A.L., Juhász G. Drosophila Arl8 is a general positive regulator of lysosomal fusion events. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019;4:533–544. - PubMed
-
- Brazill D.T., Caprette D.R., Myler H.A., Hatton R.D., Ammann R.R., Lindsey D.F., Brock D.A., Gomer R.H. A protein containing a serine-rich domain with vesicle fusing properties mediates cell cycle-dependent cytosolic pH regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:19231–19240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

