Molecular Subsets in Renal Cancer Determine Outcome to Checkpoint and Angiogenesis Blockade
- PMID: 33157048
- PMCID: PMC8436590
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.10.011
Molecular Subsets in Renal Cancer Determine Outcome to Checkpoint and Angiogenesis Blockade
Abstract
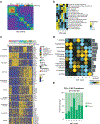
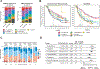
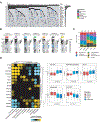
Integrated multi-omics evaluation of 823 tumors from advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) patients identifies molecular subsets associated with differential clinical outcomes to angiogenesis blockade alone or with a checkpoint inhibitor. Unsupervised transcriptomic analysis reveals seven molecular subsets with distinct angiogenesis, immune, cell-cycle, metabolism, and stromal programs. While sunitinib and atezolizumab + bevacizumab are effective in subsets with high angiogenesis, atezolizumab + bevacizumab improves clinical benefit in tumors with high T-effector and/or cell-cycle transcription. Somatic mutations in PBRM1 and KDM5C associate with high angiogenesis and AMPK/fatty acid oxidation gene expression, while CDKN2A/B and TP53 alterations associate with increased cell-cycle and anabolic metabolism. Sarcomatoid tumors exhibit lower prevalence of PBRM1 mutations and angiogenesis markers, frequent CDKN2A/B alterations, and increased PD-L1 expression. These findings can be applied to molecularly stratify patients, explain improved outcomes of sarcomatoid tumors to checkpoint blockade versus antiangiogenics alone, and develop personalized therapies in RCC and other indications.
Keywords: CDKN2A/B; PBRM1; PD-L1; VHL; atezolizumab; bevacizumab; checkpoint blockade; integrated genomics; renal cell carcinoma; sarcomatoid; sunitinib.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests R.J.M. has received honoraria for advisory roles from Roche–Genentech (RGE), Pfizer, Novartis, Exelixis, Eisai, Lilly Oncology, AstraZeneca (AZ), Incyte, and Merck Sharp & Dohme (MSD), and institutional support from Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS), RGE, Pfizer, Novartis, Exelixis, and Eisai outside of the submitted work. T.P. has received grants from AZ and RGE, and honoraria from AZ, RGE, BMS, Pfizer, Novartis, Exelixis, and MSD outside of the submitted work. DFM has received grants from BMS and Prometheus and honoraria for consulting roles from BMS, Pfizer, MSD, Novartis, Eisai, Exelixis, Array BioPharm, and RGE outside of the submitted work. M.B.A. has received grants from RGE during the conduct of the study and honoraria for consulting roles outside of the submitted work from RGE, BMS, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Exelixis, and Esai. B.E. has received grants and honoraria from BMS, Novartis, Ipsen, and EUSA outside of the submitted work. B.R. has received grants and honoraria from RGE and Pfizer during the conduct of the study and has received grants to his institution from MSD, Peloton, Aveo, BMS, AZ, and honoraria for consulting roles from Novartis, Synthorx, Compugen, Corvus, Exelixis, Arravive, Surface Oncology, 3D Medicines, and holds stock in PTC therapeutics, all outside of the submitted work. R.B., H.H., L.-F.L., N.L., A.R.A., J.F., H.K., J.L., S.M., M.G., D.T., and M.A.H. are employees of Genentech Inc. S.C. is an employee of Calithera Biosciences Inc. K.H. is an employee of Crescendo Biologics Inc. P.S.H. is an employee of Foundation Medicine Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Beuselinck B, Job S, Becht E, Karadimou A, Verkarre V, Couchy G, Giraldo N, Rioux-Leclercq N, Molinie V, Sibony M, et al. (2015). Molecular subtypes of clear cell renal cell carcinoma are associated with sunitinib response in the metastatic setting. Clin Cancer Res 21, 1329–1339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

