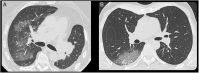
High-resolution CT features in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and negative nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swabs
- PMID: 33158785
- PMCID: PMC7577697
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2020.10.001
High-resolution CT features in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and negative nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swabs
Figures
Comment on
-
Chest CT for Typical Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia: Relationship to Negative RT-PCR Testing.Radiology. 2020 Aug;296(2):E41-E45. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020200343. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Radiology. 2020. PMID: 32049601 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . 2020. Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) when COVID-19 disease is suspected. Interim guidance. March 13.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical