Age-severity matched cytokine profiling reveals specific signatures in Covid-19 patients
- PMID: 33159040
- PMCID: PMC7646225
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-03151-z
Age-severity matched cytokine profiling reveals specific signatures in Covid-19 patients
Abstract
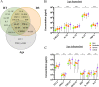
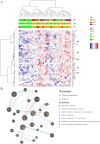
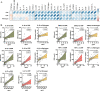
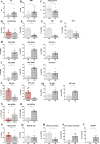
A global effort is currently undertaken to restrain the COVID-19 pandemic. Host immunity has come out as a determinant for COVID-19 clinical outcomes, and several studies investigated the immune profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infected people to properly direct the clinical management of the disease. Thus, lymphopenia, T-cell exhaustion, and the increased levels of inflammatory mediators have been described in COVID-19 patients, in particular in severe cases1. Age represents a key factor in COVID-19 morbidity and mortality2. Understanding age-associated immune signatures of patients are therefore important to identify preventive and therapeutic strategies. In this study, we investigated the immune profile of COVID-19 hospitalized patients identifying a distinctive age-dependent immune signature associated with disease severity. Indeed, defined circulating factors - CXCL8, IL-10, IL-15, IL-27, and TNF-α - positively correlate with older age, longer hospitalization, and a more severe form of the disease and may thus represent the leading signature in critical COVID-19 patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests
Figures


References
-
- Akbar AN, Gilroy DW. Aging immunity may exacerbate COVID-19. Science. 2020;369:256. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

