Besifloxacin liposomes with positively charged additives for an improved topical ocular delivery
- PMID: 33159142
- PMCID: PMC7648625
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-76381-y
Besifloxacin liposomes with positively charged additives for an improved topical ocular delivery
Abstract
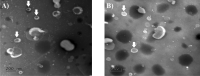
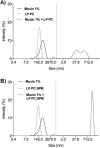
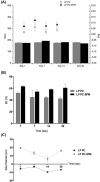
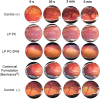
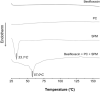
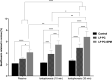
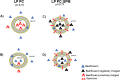
Topical ophthalmic antibiotics show low efficacy due to the well-known physiological defense mechanisms of the eye, which prevents the penetration of exogenous substances. Here, we aimed to incorporate besifloxacin into liposomes containing amines as positively charged additives and to evaluate the influence of this charge on drug delivery in two situations: (i) iontophoretic and (ii) passive treatments. Hypothesis are (i) charge might enhance the electromigration component upon current application improving penetration efficiency for a burst drug delivery, and (ii) positive charge might prolong formulation residence time, hence drug penetration. Liposomes elaborated with phosphatidylcholine (LP PC) or phosphatidylcholine and spermine (LP PC: SPM) were stable under storage at 6 ºC for 30 days, showed mucoadhesive characteristics, and were non-irritant, according to HET-CAM tests. Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy measurements showed that neither the drug nor spermine incorporations produced evident alterations in the fluidity of the liposome's membranes, which retained their structural stability even under iontophoretic conditions. Mean diameter and zeta potential were 177.2 ± 2.7 nm and - 5.7 ± 0.3 mV, respectively, for LP PC; and 175.4 ± 1.9 nm and + 19.5 ± 1.0 mV, respectively, for LP PC:SPM. The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and the minimal bactericide concentration (MBC) of the liposomes for P. aeruginosa showed values lower than the commercial formulation (Besivance). Nevertheless, both formulations presented a similar increase in permeability upon the electric current application. Hence, liposome charge incorporation did not prove to be additionally advantageous for iontophoretic therapy. Passive drug penetration was evaluated through a novel in vitro ocular model that simulates the lacrimal flow and challenges the formulation resistance in the passive delivery situation. As expected, LP PC: SPM showed higher permeation than the control (Besivance). In conclusion, besifloxacin incorporation into positively charged liposomes improved passive topical delivery and can be a good strategy to improve topical ophthalmic treatments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

