The calcium channel TRPV6 is a novel regulator of RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation and bone absorption activity through the IGF-PI3K-AKT pathway
- PMID: 33159483
- PMCID: PMC7791174
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12955
The calcium channel TRPV6 is a novel regulator of RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation and bone absorption activity through the IGF-PI3K-AKT pathway
Abstract
Objectives: Calcium ion signals are important for osteoclast differentiation. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 6 (TRPV6) is a regulator of bone homeostasis. However, it was unclear whether TRPV6 was involved in osteoclast formation. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate the role of TPRV6 in bone metabolism and to clarify its regulatory role in osteoclasts at the cellular level.
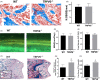
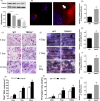
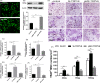
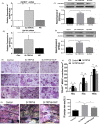
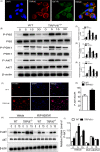
Materials and methods: Bone structure and histological changes in Trpv6 knockout mice were examined using micro-computed tomography and histological analyses. To investigate the effects of Trpv6 on osteoclast function, we silenced or overexpressed Trpv6 in osteoclasts via lentivirus transfection, respectively. Osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption viability were measured by tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining and pit formation assays. The expression of osteoclast marker genes, including cathepsin k, DC-STAMP, Atp6v0d2 and TRAP, was measured by qRT-PCR. Cell immunofluorescence and Western blotting were applied to explore the mechanisms by which the IGF-PI3K-AKT pathway was involved in the regulation of osteoclast formation and bone resorption by Trpv6.
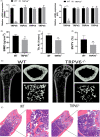
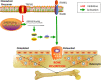
Results: We found that knockout of Trpv6 induced osteoporosis and enhanced bone resorption in mice, but did not affect bone formation. Further studies showed that Trpv6, which was distributed on the cell membrane of osteoclasts, acted as a negative regulator for osteoclast differentiation and function. Mechanistically, Trpv6 suppressed osteoclastogenesis by decreasing the ratios of phosphoprotein/total protein in the IGF-PI3K-AKT signalling pathway. Blocking of the IGF-PI3K-AKT pathway significantly alleviated the inhibitory effect of Trpv6 on osteoclasts formation.
Conclusions: Our study confirmed the important role of Trpv6 in bone metabolism and clarified its regulatory role in osteoclasts at the cellular level. Taken together, this study may inspire a new strategy for the treatment of osteoporosis.
Keywords: IGF-PI3K-AKT; TRPV6; osteoclast; osteoporosis.
© 2020 The Authors. Cell Proliferation Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Knockout of TRPV6 causes osteopenia in mice by increasing osteoclastic differentiation and activity.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33(3):796-809. doi: 10.1159/000358653. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24686448
-
New mechanistic understanding of osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption mediated by P2X7 receptors and PI3K-Akt-GSK3β signaling.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Jul 8;29(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00614-5. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38977961 Free PMC article.
-
PDK1 is important lipid kinase for RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and function via the regulation of the Akt-GSK3β-NFATc1 signaling cascade.J Cell Biochem. 2020 Nov;121(11):4542-4557. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29677. Epub 2020 Feb 12. J Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32048762
-
Regulators of osteoclast differentiation and cell-cell fusion.Keio J Med. 2011;60(4):101-5. doi: 10.2302/kjm.60.101. Keio J Med. 2011. PMID: 22200633 Review.
-
Finely-Tuned Calcium Oscillations in Osteoclast Differentiation and Bone Resorption.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 26;22(1):180. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010180. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33375370 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neoandrographolide inhibits mature osteoclast differentiation to alleviate bone loss and treat osteoporosis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 11;16:1466057. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1466057. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40008134 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the TRPV6 calcium channel-specific phenotype by RNA-seq in castration-resistant human prostate cancer cells.Front Genet. 2023 Jul 27;14:1215645. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1215645. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37576552 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting TRPC channels for control of arthritis-induced bone erosion.Sci Adv. 2025 Jan 17;11(3):eabm9843. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abm9843. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 39813349 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of calcium signaling in cancer metastasis to bone.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2022;3(4):445-462. doi: 10.37349/etat.2022.00094. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2022. PMID: 36071984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of transient receptor potential channels in chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 9;16:1583487. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1583487. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40417213 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Klein‐Nulend J, van Oers RF, Bakker AD, Bacabac RG. Bone cell mechanosensitivity, estrogen deficiency, and osteoporosis. J Biomech. 2015;48(5):855‐865. - PubMed
-
- Carey J, Buehring B. Current imaging techniques inosteoporosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018;114(5):115‐126. - PubMed
-
- Ma J, Du D, Liu J, et al. Hydrogen sulphide promotes osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting autophagy through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. J Drug Target. 2020;28(2):176‐185. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

