COVID-19 in cancer patients: clinical characteristics and outcome-an analysis of the LEOSS registry
- PMID: 33159569
- PMCID: PMC7648543
- DOI: 10.1007/s00277-020-04328-4
COVID-19 in cancer patients: clinical characteristics and outcome-an analysis of the LEOSS registry
Abstract
Introduction: Since the early SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, cancer patients have been assumed to be at higher risk for severe COVID-19. Here, we present an analysis of cancer patients from the LEOSS (Lean European Open Survey on SARS-CoV-2 Infected Patients) registry to determine whether cancer patients are at higher risk.
Patients and methods: We retrospectively analyzed a cohort of 435 cancer patients and 2636 non-cancer patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection, enrolled between March 16 and August 31, 2020. Data on socio-demographics, comorbidities, cancer-related features and infection course were collected. Age-, sex- and comorbidity-adjusted analysis was performed. Primary endpoint was COVID-19-related mortality.
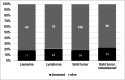
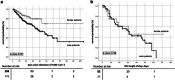
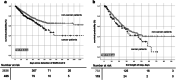
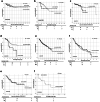
Results: In total, 435 cancer patients were included in our analysis. Commonest age category was 76-85 years (36.5%), and 40.5% were female. Solid tumors were seen in 59% and lymphoma and leukemia in 17.5% and 11% of patients. Of these, 54% had an active malignancy, and 22% had recently received anti-cancer treatments. At detection of SARS-CoV-2, the majority (62.5%) presented with mild symptoms. Progression to severe COVID-19 was seen in 55% and ICU admission in 27.5%. COVID-19-related mortality rate was 22.5%. Male sex, advanced age, and active malignancy were associated with higher death rates. Comparing cancer and non-cancer patients, age distribution and comorbidity differed significantly, as did mortality (14% vs 22.5%, p value < 0.001). After adjustments for other risk factors, mortality was comparable.
Conclusion: Comparing cancer and non-cancer patients, outcome of COVID-19 was comparable after adjusting for age, sex, and comorbidity. However, our results emphasize that cancer patients as a group are at higher risk due to advanced age and pre-existing conditions.
Keywords: Adjusted analysis; COVID-19; Cancer patients; Cohort study; LEOSS; Pandemic; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
MMR has received research funding from the Interdisciplinary Centre for Clinical Research (IZKF) Jena and honoraria from Janssen, outside the submitted work GB reports grants from German Federal Ministry of Research & Education and Federal Ministry of Health, personal fee from Jazz Pharmaceuticals, MSD, and NewConceptOncology all outside the submitted work. FH received lecture and other honoraria from Correvio, Infectopharm, and Novartis, outside the submitted work. PK has received non-financial scientific grants from Miltenyi Biotec GmbH, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany, and the Cologne Excellence Cluster on Cellular Stress Responses in Aging-Associated Diseases, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany, and received lecture honoraria from or is advisor to Akademie für Infektionsmedizin e.V., Astellas Pharma, European Confederation of Medical Mycology, Gilead Sciences, GPR Academy Ruesselsheim, MSD Sharp & Dohme GmbH, Noxxon N.V., and University Hospital, LMU Munich outside the submitted work. MvLT has received travel grants and honoraria from Celgene, Gilead, Chugai, Janssen, Novartis, Amgen, Takeda, BMS, Medac, Oncopeptides, Merck, CDDF, Pfizer, is a consultant for Celgene, Gilead, Oncopeptides, MSD, 4DPharma, Janssen, Shionogi and received research funding from BMBF, Deutsche Jose Carreras Leukämie-Stiftung, IZKF Jena, DFG, Novartis, Gilead, Deutsche Krebshilfe, Celgene, Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, outside the submitted work. All other corresponding authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, E (2020) [cited 2020 04.10.2020]; Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19-pandemic)
-
- Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J, Wang B, Xiang H, Cheng Z, Xiong Y, Zhao Y, Li Y, Wang X, Peng Z. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020;323(11):1061–1069. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.1585. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, Shu H, Xia J', Liu H, Wu Y, Zhang L, Yu Z, Fang M, Yu T, Wang Y, Pan S, Zou X, Yuan S, Shang Y. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(5):475–481. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dai M, Liu D, Liu M, Zhou F, Li G, Chen Z, Zhang Z, You H, Wu M, Zheng Q, Xiong Y, Xiong H, Wang C, Chen C, Xiong F, Zhang Y, Peng Y, Ge S, Zhen B, Yu T, Wang L, Wang H, Liu Y, Chen Y, Mei J, Gao X, Li Z, Gan L, He C, Li Z, Shi Y, Qi Y, Yang J, Tenen DG, Chai L, Mucci LA, Santillana M, Cai H. Patients with cancer appear more vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2: a multicenter study during the COVID-19 outbreak. Cancer Discov. 2020;10(6):783–791. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

