Single-Cell Profiling of Ebola Virus Disease In Vivo Reveals Viral and Host Dynamics
- PMID: 33159858
- PMCID: PMC7707107
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.002
Single-Cell Profiling of Ebola Virus Disease In Vivo Reveals Viral and Host Dynamics
Abstract
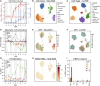
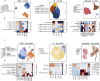
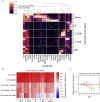
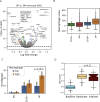
Ebola virus (EBOV) causes epidemics with high mortality yet remains understudied due to the challenge of experimentation in high-containment and outbreak settings. Here, we used single-cell transcriptomics and CyTOF-based single-cell protein quantification to characterize peripheral immune cells during EBOV infection in rhesus monkeys. We obtained 100,000 transcriptomes and 15,000,000 protein profiles, finding that immature, proliferative monocyte-lineage cells with reduced antigen-presentation capacity replace conventional monocyte subsets, while lymphocytes upregulate apoptosis genes and decline in abundance. By quantifying intracellular viral RNA, we identify molecular determinants of tropism among circulating immune cells and examine temporal dynamics in viral and host gene expression. Within infected cells, EBOV downregulates STAT1 mRNA and interferon signaling, and it upregulates putative pro-viral genes (e.g., DYNLL1 and HSPA5), nominating pathways the virus manipulates for its replication. This study sheds light on EBOV tropism, replication dynamics, and elicited immune response and provides a framework for characterizing host-virus interactions under maximum containment.
Keywords: CyTOF; Ebola virus; Seq-Well; bystander cells; host-virus interactions; interferon; monocytes; scRNA-Seq; single-cell; viral tropism.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests A.K.S. has received compensation for consulting and SAB membership from Honeycomb Biotechnologies, Cellarity, Ochre Bio, Repertoire, and Dahlia Biosciences.
Figures












References
-
- Al Sayed M.F., Amrein M.A., Bührer E.D., Huguenin A.L., Radpour R., Riether C., Ochsenbein A.F. T-cell-Secreted TNFα Induces Emergency Myelopoiesis and Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Differentiation in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019;79:346–359. - PubMed
-
- Baize S., Leroy E.M., Georges-Courbot M.C., Capron M., Lansoud-Soukate J., Debré P., Fisher-Hoch S.P., McCormick J.B., Georges A.J. Defective humoral responses and extensive intravascular apoptosis are associated with fatal outcome in Ebola virus-infected patients. Nat. Med. 1999;5:423–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

