NEDD8 and ubiquitin ligation by cullin-RING E3 ligases
- PMID: 33160249
- PMCID: PMC8096640
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2020.10.007
NEDD8 and ubiquitin ligation by cullin-RING E3 ligases
Abstract
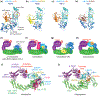
RING E3s comprise the largest family of ubiquitin (UB) and ubiquitin-like protein (UBL) ligases. RING E3s typically promote UB or UBL transfer from the active site of an associated E2 enzyme to a distally-recruited substrate. Many RING E3s - including the cullin-RING ligase family - are multifunctional, interacting with various E2s (or other E3s) to target distinct proteins, transfer different UBLs, or to initially modify substrates with UB or subsequently elongate UB chains. Here we consider recent structures of cullin-RING ligases, and their partner E2 enzymes, representing ligation reactions. The studies collectively reveal multimodal mechanisms - interactions between ancillary E2 or E3 domains, post-translational modifications, or auxiliary binding partners - directing cullin-RING E3-E2 enzyme active sites to modify their specific targets.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures



References
-
- Pan ZQ, Kentsis A, Dias DC, Yamoah K, Wu K: Nedd8 on cullin: building an expressway to protein destruction. Oncogene 2004, 23:1985–1997. - PubMed
-
- Komander D, Rape M: The ubiquitin code. Annu Rev Biochem 2012, 81:203–229. - PubMed
-
- Pruneda JN, Littlefield PJ, Soss SE, Nordquist KA, Chazin WJ, Brzovic PS, Klevit RE: Structure of an E3:E2~Ub complex reveals an allosteric mechanism shared among RING/U-box ligases. Mol Cell 2012, 47:933–942. - PMC - PubMed
-
A NMR-based study and structural model defining a key hydrogen bond between a conserved side chain within E3s and carbonyl of E2s for stabilizing the closed E2~UB conformation.
-
- Hamilton KS, Ellison MJ, Barber KR, Williams RS, Huzil JT, McKenna S, Ptak C, Glover M, Shaw GS: Structure of a conjugating enzyme-ubiquitin thiolester intermediate reveals a novel role for the ubiquitin tail. Structure 2001, 9:897–904. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

