Combination blockade of OX40L and CD30L inhibits allergen-driven memory TH2 cell reactivity and lung inflammation
- PMID: 33160971
- PMCID: PMC8096862
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.10.037
Combination blockade of OX40L and CD30L inhibits allergen-driven memory TH2 cell reactivity and lung inflammation
Abstract
Background: The selective reduction of memory TH2 cell responses could be key to affording tolerance and protection from the recurrence of damaging allergic pathology.
Objective: We asked whether TNF family costimulatory molecules cooperated to promote accumulation and reactivity of effector memory CD4 T cells to inhaled complex allergen, and whether their neutralization could promote airway tolerance to subsequent reexposure to allergen.
Methods: Mice were sensitized intraperitoneally or intranasally with house dust mite and challenged with intranasal allergen after memory had developed. We assessed whether single or combined blockade of OX40L/CD252 and CD30L/CD153 inhibited memory T cells from driving acute asthmatic lung inflammation and protected mice following exposure to allergen at a later time.
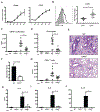
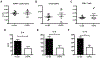
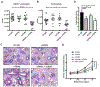
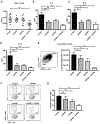
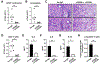
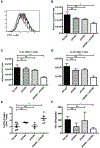
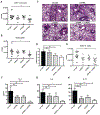
Results: OX40- or CD30-deficient animals showed strong or partial protection against allergic airway inflammation; however, neutralizing either molecule alone during the secondary response to allergen had little effect on the frequency of effector memory CD4 T cells formed and acute lung inflammation. In contrast, a significant reduction in eosinophilic inflammation was observed when OX40L and CD30L were simultaneously neutralized, with dual blockade inhibiting effector memory TH2 cell expansion in the lungs, whereas formation of peripherally induced regulatory T cells remained intact. Moreover, dual blockade during the secondary response resulted in a tolerogenic state such that mice did not develop a normal tertiary memory TH2 cell and lung inflammatory response when challenged weeks later with allergen.
Conclusion: Memory T-cell responses to complex allergens are controlled by several TNF costimulatory interactions, and their combination targeting might represent a strategy to reduce the severity of inflammatory reactions following reexposure to allergen.
Keywords: Allergen; CD30L; OX40L; T(H)2 cell; TNF family; asthma; memory.
Copyright © 2020 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of potential conflict of interest: Michael Croft has patents on OX40/OX40L. All other authors declare that they have no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Walsh GM. Biologics targeting IL-5, IL-4 or IL-13 for the treatment of asthma - an update. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2017; 13:143–9. - PubMed
-
- Fajt ML, Wenzel SE. Asthma phenotypes and the use of biologic medications in asthma and allergic disease: the next steps toward personalized care. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2015; 135:299–310; quiz 1. - PubMed
-
- Lambrecht BN, Hammad H. The immunology of asthma. Nat Immunol 2015; 16:45–56. - PubMed
-
- Leomicronn B T Cells in Allergic Asthma: Key Players Beyond the Th2 Pathway. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2017; 17:43. - PubMed
-
- Akdis CA, Akdis M. Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy. The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology 2011; 127:18–27; quiz 8–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

