Effect of 3-subsitution of quinolinehydroxamic acids on selectivity of histone deacetylase isoforms
- PMID: 33161799
- PMCID: PMC7655065
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1839446
Effect of 3-subsitution of quinolinehydroxamic acids on selectivity of histone deacetylase isoforms
Abstract
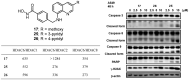
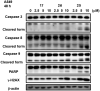
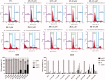
A series of 3-subsituted quinolinehydroxamic acids has been synthesised and evaluated for their effect on human lung cancer cell line (A549), human colorectal cancer cell line (HCT116) and HDAC isoforms 1, 2, 6, and 8. The results indicated that substitution at C3 of quinoline is favoured for HDAC6 selectivity. Two compounds (25 and 26) were also found to be potent anti-proliferative compounds with IC50 values ranging from 1.29 to 2.13 µM against A549 and HCT116 cells. These compounds displayed remarkable selectivity for HDAC6 over other HDAC isoforms with nanomolar IC50 values. Western blot analysis revealed that compounds of this series activate apoptotic caspase pathway as indicated by cleavage of caspase 3, 8, and 9 and also increase phosphorylated H2AX thus inducing DNA double strand fragmentation in a concentration dependent manner. Flow cytometric analysis also displayed a dose dependent increase of cell population in sub G1 phase.
Keywords: HDAC; Quinoline; acrylamide; colon cancer; hydroxamic acid; lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Barnes P, Adcock IM, Ito K.. Histone acetylation and deacetylation: importance in inflammatory lung diseases. Eur Resp J 2005;25:552–63. - PubMed
-
- Dokmanovic M, Clark C, Marks PA.. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: overview andperspectives. Mol Cancer Res 2007;5:981–9. - PubMed
-
- Adcock IM, Ito K, Barnes PJ.. Histone deacetylation: an important mechanism in inflammatory lung diseases. COPD 2005;2:445–55. - PubMed
-
- (a) Mehndiratta S, Pan SL, Kumar S, et al. . Indole-3-ethylsulfamoylphenylacrylamides with potent anti-proliferative and anti-angiogenic activities. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 2016;16:907–13. - PubMed
- (b) Huang YC, Huang FI, Mehndiratta S, et al. . Anticancer activity of MPT0G157, a derivative of indolylbenzenesulfonamide, inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis. Oncotarget 2015;6:18590–601. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
