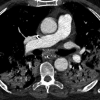
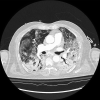
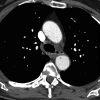
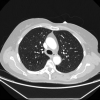
Could Bronchial Artery Embolization Be a Modality for Treating Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2?
- PMID: 33162308
- PMCID: PMC7448871
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2020.08.022
Could Bronchial Artery Embolization Be a Modality for Treating Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2?
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bronchial Artery Embolization Performed in COVID-19 Patients: Tolerance and Outcomes.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2020 Dec;43(12):1949-1951. doi: 10.1007/s00270-020-02621-3. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32851427 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Lung Ultrasound for Treatment of Patients With COVID-19: Please Report Your Settings and Mechanical Index.J Ultrasound Med. 2021 Jan;40(1):187-189. doi: 10.1002/jum.15389. Epub 2020 Jul 21. J Ultrasound Med. 2021. PMID: 32691856 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pulmonary embolism in patients with COVID-19: Time to change the paradigm of computed tomography.Thromb Res. 2020 Jun;190:58-59. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.011. Epub 2020 Apr 11. Thromb Res. 2020. PMID: 32302782 Free PMC article.
-
CT Findings of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Severe Pneumonia.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020 May;214(5):W85-W86. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.23035. Epub 2020 Mar 24. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020. PMID: 32208010 No abstract available.
-
[Update 2021: Pulmonary Sequelae of COVID-19 Pneumonia].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2021 Jul;146(13-14):927-932. doi: 10.1055/a-1449-5158. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2021. PMID: 34256411 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Synapomorphic features of hepatic and pulmonary vasculatures include comparable purinergic signaling responses in host defense and modulation of inflammation.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021 Aug 1;321(2):G200-G212. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00406.2020. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34105986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Case Reports: Bronchial Mucosal Vasculature Is Also Involved in the Acute Vascular Distress Syndrome of COVID-19.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 30;8:710992. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.710992. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34917628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Song L.C., Chen X.X., Meng J.G. Effects of different corticosteroid doses and durations on smoke inhalation-induced acute lung injury and pulmonary fibrosis in the rat. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;71:392–403. - PubMed
-
- Park M.S., Cancio L.C., Batchinsky A.I. Assessment of severity of ovine smoke inhalation injury by analysis of computed tomographic scans. J Trauma. 2003;55:417–427. discussion 427–429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

