The role of m6A modification in physiology and disease
- PMID: 33162550
- PMCID: PMC7649148
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-03143-z
The role of m6A modification in physiology and disease
Abstract
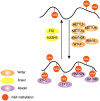
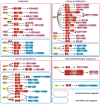
Similar to DNA epigenetic modifications, multiple reversible chemical modifications on RNAs have been uncovered in a new layer of epigenetic modification. N6-methyladenosine (m6A), a modification that occurs in ~30% transcripts, is dynamically regulated by writer complex (methylase) and eraser (RNA demethylase) proteins, and is recognized by reader (m6A-binding) proteins. The effects of m6A modification are reflected in the functional modulation of mRNA splicing, export, localization, translation, and stability by regulating RNA structure and interactions between RNA and RNA-binding proteins. This modulation is involved in a variety of physiological behaviors, including neurodevelopment, immunoregulation, and cellular differentiation. The disruption of m6A modulations impairs gene expression and cellular function and ultimately leads to diseases such as cancer, psychiatric disorders, and metabolic disease. This review focuses on the mechanisms and functions of m6A modification in a variety of physiological behaviors and diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

