Trust and compliance to public health policies in times of COVID-19
- PMID: 33162621
- PMCID: PMC7598751
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpubeco.2020.104316
Trust and compliance to public health policies in times of COVID-19
Abstract
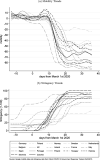
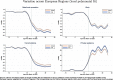
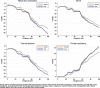
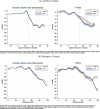
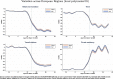
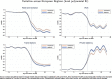
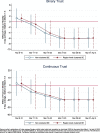
While degraded trust and cohesion within a country are often shown to have large socio-economic impacts, they can also have dramatic consequences when compliance is required for collective survival. We illustrate this point in the context of the COVID-19 crisis. Policy responses all over the world aim to reduce social interaction and limit contagion. Using data on human mobility and political trust at regional level in Europe, we examine whether the compliance to these containment policies depends on the level of trust in policy makers prior to the crisis. Using a double difference approach around the time of lockdown announcements, we find that high-trust regions decrease their mobility related to non-necessary activities significantly more than low-trust regions. We also exploit country and time variation in treatment using the daily strictness of national policies. The efficiency of policy stringency in terms of mobility reduction significantly increases with trust. The trust effect is nonlinear and increases with the degree of stringency. We assess how the impact of trust on mobility potentially translates in terms of mortality growth rate.
Keywords: COVID-19; Policy stringency; Political trust.
© 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Algan Y., Cahuc P. Civic virtue and labor market institutions. Am. Econ. J. Macroecon. 2009;1(1):111–145.
-
- Algan Y., Cahuc P. vol. 2. Elsevier; 2014. Trust, growth, and well-being: New evidence and policy implications. (Handbook of Economic Growth). pp. 49–120.
-
- Algan Y., Malgouyres C., Senik C. Territories, well-being and public policy. Notes du conseil d’analyse économique. 2019;7:1–12.
-
- Askitas N., Tatsiramos K., Verheyden B. Lockdown strategies, mobility patterns and Covid-19. Covid Econ. Vetted Real-Time Papers. 2020;23:263–302.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

