Expression of AIM2 in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Role on Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes
- PMID: 33162829
- PMCID: PMC7605934
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/1693730
Expression of AIM2 in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Role on Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes
Abstract
Objectives: To determine differences in AIM2 inflammasome expression levels between rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA) and to investigate the role of AIM2 in RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RA-FLS).
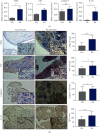
Methods: Serum AIM2 levels among health controls (HC, n = 20), OA (n = 25), and RA (n =49) patients were compared via ELISA. The different expression levels of AIM2, ASC, caspase-1, and IL-1β between RA and OA synovium were semiquantified by qRT-PCR and immunohistochemical (IHC) staining. IHC staining was recorded by H scores, and its correlation with the ESR and CRP levels of RA patients was determined. SiRNA AIM2 was transferred to RA-FLS and its effects on the proliferation and migration via CCK-8 assay and Transwell test, respectively.
Results: In RA sera, the HC expressed higher level of AIM2 than OA and RA patients, and ASC, caspase-1, and IL-1β expressed higher in RA patients than HC; no significant differences were observed between sera of OA and RA patients. However, in affected knee synovium, AIM2, ASC, caspase-1, and IL-1β were expressed higher in RA than that of OA. Moreover, the H scores of AIM2, ASC, and IL-1β were positively correlated with the ESR and CRP levels in RA patients. The proliferation of FLS was significantly inhibited after transferring with AIM2 siRNA to FLS. There were no differences in apoptosis and migration assay between the si-AIM2 group and the control group.
Conclusion: AIM2 inflammasome pathway involves in the pathogenesis of RA. si-AIM2 inhibits the proliferation of RA-FLS, which may be a promising therapeutic strategy for the treatment of RA.
Copyright © 2020 Yong Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures




References
-
- Calabresi E., Petrelli F., Bonifacio A. F., Puxeddu I., Alunno A. One year in review 2018: pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. 2018;36(2):175–184. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

