Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts-Derived Exosomes Suppress Immune Cell Function in Breast Cancer via the miR-92/PD-L1 Pathway
- PMID: 33162971
- PMCID: PMC7581790
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02026
Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts-Derived Exosomes Suppress Immune Cell Function in Breast Cancer via the miR-92/PD-L1 Pathway
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived exosomes suppress immune cell function in breast cancer via the miR-92/PD-L1 pathway.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 30;15:1469689. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1469689. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39139568 Free PMC article.
Abstract
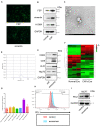
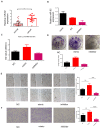
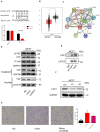
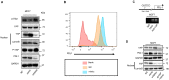
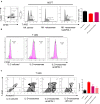
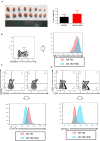
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are an essential component in the tumor microenvironment and have been reported to contribute to tumor progression through many mechanisms; however, the detailed mechanism underlying the immune-suppression effect of CAFs is not clearly defined. In this study, human breast cancer-derived CAFs were cultured, and CAF-derived exosomes in a culture medium were isolated. Using a miRNA profiles assay, we identify a significantly higher level of microRNA-92 isolated in CAFs exosomes. After treatment by CAF-derived exosomes, breast cancer cells express higher programmed cell death receptor ligand 1 (PD-L1), accompanied with increased miR-92 expression. Increased PD-L1 expression, which was induced by CAF-derived exosomes, significantly promotes apoptosis and impaired proliferation of T cells. The underlying mechanism of this effect was studied, proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells were increased after the transfection of miR-92, LATS2 was recognized as a target gene of miR-92, and further confirmed by a luciferase assay. Immunoprecipitation showed that LATS2 can interact with YAP1, chromatin immunoprecipitation confirmed that after nuclear translocation YAP1 could bind to the enhancer region of PD-L1 to promotes transcription activity. Furthermore, the animal study confirmed that CAFs significantly promoted tumor progression and impaired the function of tumor-infiltrated immune cells in vivo. Our data revealed a novel mechanism that can induce immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment.
Keywords: CAF; PD-L1; YAP1; breast cancer; miR-92.
Copyright © 2020 Dou, Ren, Han, Xu, Ge, Gu and Wang.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

