The Role of GITR/GITRL Interaction in Autoimmune Diseases
- PMID: 33163004
- PMCID: PMC7581784
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.588682
The Role of GITR/GITRL Interaction in Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
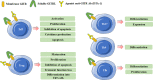
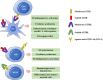
Glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein (GITR) is a member of the TNFR superfamily which is expressed in various cells, including T cells, natural killer cells and some myeloid cells. GITR is activated by its ligand, GITRL, mainly expressed on antigen presenting cells and endothelial cells. It has been acknowledged that the engagement of GITR can modulate both innate and adaptive immune responses. Accumulated evidence suggests GITR/GITRL interaction is involved in the pathogenesis of tumor, inflammation and autoimmune diseases. In this review, we describe the effects of GITR/GITRL activation on effector T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs) and myeloid cells; summarize its role and the underlying mechanisms in modulating autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: GITRL; T cell; autoimmune diseases; glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein; myeloid cells.
Copyright © 2020 Tian, Zhang, Rui and Wang.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of the glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein (GITR)-GITR ligand pathway in innate and adaptive immunity.Crit Rev Immunol. 2010;30(6):547-57. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v30.i6.40. Crit Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21175417 Review.
-
Pharmacological modulation of GITRL/GITR system: therapeutic perspectives.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Apr;165(7):2089-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01753.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22029729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GITR: a modulator of immune response and inflammation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;647:156-73. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-89520-8_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19760073 Review.
-
GITR ligand fusion protein agonist enhances the tumor antigen-specific CD8 T-cell response and leads to long-lasting memory.J Immunother Cancer. 2017 Jun 20;5:47. doi: 10.1186/s40425-017-0247-0. eCollection 2017. J Immunother Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28649380 Free PMC article.
-
GITR/GITRL: more than an effector T cell co-stimulatory system.Eur J Immunol. 2007 May;37(5):1165-9. doi: 10.1002/eji.200636933. Eur J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17407102 Review.
Cited by
-
MDM4 was associated with poor prognosis and tumor-immune infiltration of cancers.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jan 27;29(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01684-z. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38281029 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: The Emerging Cornerstone in Cholangiocarcinoma Therapy?Liver Cancer. 2021 Sep 21;10(6):545-560. doi: 10.1159/000518104. eCollection 2021 Nov. Liver Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34950178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation Markers on B and T Cells and Immune Checkpoints in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 4;23(15):8656. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158656. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroinflammation: Extinguishing a blaze of T cells.Immunol Rev. 2022 Oct;311(1):151-176. doi: 10.1111/imr.13122. Epub 2022 Jul 31. Immunol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35909230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Costimulatory and Coinhibitory Immune Checkpoints in Atherosclerosis: Therapeutic Targets in Atherosclerosis?JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2024 Mar 13;9(6):827-843. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2023.12.007. eCollection 2024 Jun. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39070270 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

