Pembrolizumab-Induced Psoriasis in Metastatic Melanoma: Activity and Safety of Apremilast, a Case Report
- PMID: 33163407
- PMCID: PMC7591674
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.579445
Pembrolizumab-Induced Psoriasis in Metastatic Melanoma: Activity and Safety of Apremilast, a Case Report
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors targeting cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4), programmed death-1 receptor (PD-1), and programmed death-1 receptor and its ligand (PD-L1) increased the survival of patients affected by metastatic malignant melanoma. Due to their mechanism of action, these drugs are associated with a unique toxicity profile. Indeed, immune-related adverse events (irAEs) present a wide clinical spectrum representing the Achilles' heel of immunotherapy. Overall, cutaneous toxicities are among the most common irAEs. Immunomodulatory drugs are used for the management of irAEs and can theoretically lead to tumor escape.
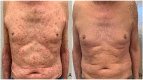
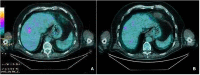
Case presentation: We report the case of a 75-year-old man with metastatic melanoma receiving the anti-PD1 Pembrolizumab therapy. After 10 treatment cycles, the patient came to our clinic with itchy psoriatic manifestations widespread >30% of the body surface [12.3 Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score] that negatively impacted on the patient's quality of life and compliance with immunotherapy. Additionally, he had no positive personal history of psoriasis. Given the severity of the cutaneous manifestations, in a multidisciplinary approach, Apremilast (an oral small molecule PDE4 inhibitor) was started. Furthermore, Pembrolizumab was interrupted for 4 weeks until the improvement of skin lesions and the disappearance of itching. Immunosuppressive methylprednisolone therapy was initiated with a dose of 16 mg/die; then, this initial dose was progressively reduced until discontinuation. After 10 months, the patient had a good general clinical condition with psoriasis complete remission. Moreover, positron emission tomography (PET) and computed tomography (CT) scans showed complete response by immune Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (iRECIST).
Conclusion: To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on the safety and efficacy of Apremilast for the treatment of immunotherapy-induced psoriasis in metastatic melanoma.
Keywords: Apremilast; Pembrolizumab; checkpoint inhibitors; cutaneous immune-related adverse events; immune-related adverse events; immunotherapy; melanoma; psoriasis.
Copyright © 2020 Siciliano, Dastoli, d’Apolito, Staropoli, Tassone, Tagliaferri and Barbieri.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

