Increase in bone turnover markers in HIV patients treated with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate combined with raltegravir or efavirenz
- PMID: 33163587
- PMCID: PMC7607241
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bonr.2020.100727
Increase in bone turnover markers in HIV patients treated with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate combined with raltegravir or efavirenz
Abstract
Introduction: Accelerated bone loss and osteoporosis are multifactorial comorbidities related to HIV and its treatments; however, their mechanisms remain elusive. Identifying HIV treatments that are differentially linked to osteoporosis risk, and clinical factors associated with HIV-related osteoporosis may enable optimizing anti-retroviral treatment (ART) and anti-osteoporosis therapy in preventing or treating this debilitating complication. This study aims to evaluate the dynamics of bone turnover markers after initiation of two commonly used antiretroviral regimens.
Methods: A prospective matched cohort study. Thirty treatment-naïve male patients (mean age 40 ± 10y) who initiated treatment with truvada (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF)/emtricitabine (FTC)) + raltegravir or TDF/FTC + efavirenz were included in the study. Control group included 15 treatment-naive HIV patients. Serum morning fasting level of P1NP and CTX were measured 0, 1, 6, and 12 months after treatment initiation in the two study groups, and at 0, 6 and 12 months in the control group.
Results: In both treatment groups, but not in the control group, both markers increased significantly over time with no difference in BTM between patients treated with raltegravir or efavirenz. Levels of P1NP were statistically higher at 6 and 12 months after treatment initiation in both treatment groups compared to the controls, while CTX during treatment increased in both treatment groups but was significantly higher only in the raltegravir treatment group after 12 months. The ratio of area under the curve of P1NP/CTX correlated with CD4 increment.
Conclusions: Treatment initiation with raltegravir or efavirenz combined with TDF/FTC is associated with increased bone turnover. Thus, therapy that optimize bone turnover is needed to reduce bone loss at this vulnerable period and improve long-term bone health.
Keywords: CTX; Efavirenz; HIV; P1NP; Raltegravir; Tenofovir/emtricitabine.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures
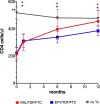
 CD4 levels increased significantly in the raltegravir/TDF + FTC [RAL] C in each time point-1, 6, 12 in comparison to treatment initiation (p = 0.009, p = 0.004, p < 0.001 respectively).
CD4 levels increased significantly in the raltegravir/TDF + FTC [RAL] C in each time point-1, 6, 12 in comparison to treatment initiation (p = 0.009, p = 0.004, p < 0.001 respectively).  CD4 levels increased significantly in the efavirenz/TDF/FTC [EFV] in each time point-1, 6, 12 in comparison to treatment initiation (p < 0.001, p = 0.003, p < 0.001 respectively). Bars indicate SD.
CD4 levels increased significantly in the efavirenz/TDF/FTC [EFV] in each time point-1, 6, 12 in comparison to treatment initiation (p < 0.001, p = 0.003, p < 0.001 respectively). Bars indicate SD.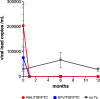
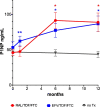
 P1NP level increased significantly in the raltegravir/TDF/FTC [RAL] group after 6 and 12 months of treatment in comparison to treatment initiation (6 months vs treatment initiation p = 0.006, 12 months vs treatment initiation p = 0.006) and to the control group (RAL vs control 6 months p = 0.002, RAL vs control 12 months p = 0.01).
P1NP level increased significantly in the raltegravir/TDF/FTC [RAL] group after 6 and 12 months of treatment in comparison to treatment initiation (6 months vs treatment initiation p = 0.006, 12 months vs treatment initiation p = 0.006) and to the control group (RAL vs control 6 months p = 0.002, RAL vs control 12 months p = 0.01).  P1NP level increased significantly in the efavirenz/TDF/FTC [EFV] after 6 and 12 months of treatment compared to treatment initiation (6 months vs treatment initiation p = 0.001, 12 months vs treatment initiation p = 0.001) and the control group (EFV vs control 6 months p = 0.005, EFV vs control 12 months p = 0.001).
P1NP level increased significantly in the efavirenz/TDF/FTC [EFV] after 6 and 12 months of treatment compared to treatment initiation (6 months vs treatment initiation p = 0.001, 12 months vs treatment initiation p = 0.001) and the control group (EFV vs control 6 months p = 0.005, EFV vs control 12 months p = 0.001).  P1NP levels were significantly higher in the efavirenz/TDF/FTC group in comparison to raltegravir/TDF/FTC [RAL] after 1 months of treatment. p = 0.004, but not at other time points (6 months p = 0.3, 12 months p = 0.7). Bars indicate SD.
P1NP levels were significantly higher in the efavirenz/TDF/FTC group in comparison to raltegravir/TDF/FTC [RAL] after 1 months of treatment. p = 0.004, but not at other time points (6 months p = 0.3, 12 months p = 0.7). Bars indicate SD.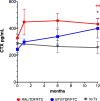
 CTX levels increased significantly in the raltegravir/TDF/FTC [RAL] in 12 months of treatment in comparison to treatment initiation (p = 0.5).
CTX levels increased significantly in the raltegravir/TDF/FTC [RAL] in 12 months of treatment in comparison to treatment initiation (p = 0.5).  CTX levels increased significantly in the raltegravir/TDF/FTC [RAL] at 12 months of treatment in comparison to the control group (untreated patients) (p = 0.02).There was no significant difference in CTX levels between RAL vs EFV in any of time points 0, 1, 6, 12 (p = 0.26, p = 0.6, p = 0.22, p = 0.53 respectively). Bars indicate SD.
CTX levels increased significantly in the raltegravir/TDF/FTC [RAL] at 12 months of treatment in comparison to the control group (untreated patients) (p = 0.02).There was no significant difference in CTX levels between RAL vs EFV in any of time points 0, 1, 6, 12 (p = 0.26, p = 0.6, p = 0.22, p = 0.53 respectively). Bars indicate SD.References
-
- Bernardino J.I. Bone mineral density and inflammatory and bone biomarkers after darunavir-ritonavir combined with either raltegravir or tenofovir-emtricitabine in antiretroviral-naive adults with HIV-1: a substudy of the NEAT001/ANRS143 randomised trial. Lancet HIV. 2015;2:e464–e473. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(15)00181-2. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

