The role of estrogen receptors in rat Sertoli cells at different stages of development
- PMID: 33163677
- PMCID: PMC7609458
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05363
The role of estrogen receptors in rat Sertoli cells at different stages of development
Abstract
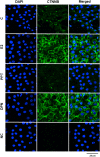
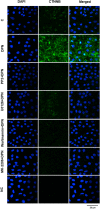
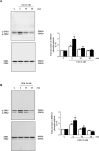
The aim of the study was to investigate the effects of estrogen receptors (ESR1 and ESR2) on the expression of the proteins involved with proliferation (CCND1) and differentiation (CDKN1B and CTNNB) of Sertoli cells from rat in different stages of development. ESR1-selective agonist PPT, but not ESR2-selective agonist DPN, increased CCND1 expression in Sertoli cells from 5- and 15-day old rats. PPT did not have any effect on CCND1 expression in Sertoli cells from 20- and 30-day-old rats. DPN, but not PPT, increased CDKN1B expression in Sertoli cells from 15-, 20-, 30-day-old rats. DPN did not have any effect on Sertoli cells from 5-day-old rats. 17β-estradiol (E2) and PPT enhanced the [Methyl-3H] thymidine incorporation in Sertoli cells from 15-day-old rats, whereas the treatment did not have any effect in 20-day-old rats. E2 and DPN, but not PPT, increased non-phosphorylated CTNNB expression in Sertoli cells from 20-day-old rats. This upregulation was blocked by ESR2-selective antagonist PHTPP. The activation of ESR1 and ESR2, respectively, plays a role in the proliferation and differentiation of Sertoli cells in a critical period of testicular development. Furthermore, in Sertoli cells from 20-day-old rats, upregulation of non-phosphorylated CTNNB by E2/ESR2, via c-SRC/ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT, may play a role in the interaction between Sertoli cells and/or in cell-germ cell adhesion and/or in the stabilization and accumulation of CTNNB in the cytosol. CTNNB could be translocated to the nucleus and modulate the transcriptional activity of specific target genes. The present study reinforces the important role of estrogen in normal testis development.
Keywords: 17β-estradiol; Cell biology; Cell culture; Cell differentiation; Estrogen receptors; Reproductive hormone; Reproductive medicine; Sertoli cells; Steroid hormones; Systems biology.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Figures







Similar articles
-
Differential role of the estrogen receptors ESR1 and ESR2 on the regulation of proteins involved with proliferation and differentiation of Sertoli cells from 15-day-old rats.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014 Jan 25;382(1):84-96. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.09.015. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24056172
-
17Beta-estradiol signaling and regulation of proliferation and apoptosis of rat Sertoli cells.Biol Reprod. 2012 Apr 12;86(4):108. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.111.096891. Print 2012 Apr. Biol Reprod. 2012. PMID: 22219213
-
17beta-estradiol induces the translocation of the estrogen receptors ESR1 and ESR2 to the cell membrane, MAPK3/1 phosphorylation and proliferation of cultured immature rat Sertoli cells.Biol Reprod. 2008 Jan;78(1):101-14. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.107.063909. Epub 2007 Oct 10. Biol Reprod. 2008. PMID: 17928626
-
Expression and signaling of G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER) in rat sertoli cells.Biol Reprod. 2010 Aug 1;83(2):307-17. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.084160. Epub 2010 May 5. Biol Reprod. 2010. PMID: 20445128
-
Differential modulation of gonadotropin secretion by selective estrogen receptor 1 and estrogen receptor 2 agonists in ovariectomized ewes.Biol Reprod. 2007 Aug;77(2):320-8. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.107.060046. Epub 2007 Apr 11. Biol Reprod. 2007. PMID: 17429013
Cited by
-
Assessment of Zearalenone-Induced Cell Survival and of Global Gene Regulation in Mouse TM4 Sertoli Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Jan 26;14(2):98. doi: 10.3390/toxins14020098. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35202126 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear and Membrane Receptors for Sex Steroids Are Involved in the Regulation of Delta/Serrate/LAG-2 Proteins in Rodent Sertoli Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 18;23(4):2284. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042284. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216398 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Mechanism of Sex Hormones on Sertoli Cell Development and Proliferation.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jul 23;12:648141. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.648141. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34367061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway: How does it regulate development of Sertoli cells and spermatogenic cells?Histol Histopathol. 2022 Jul;37(7):621-636. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-457. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Histol Histopathol. 2022. PMID: 35388905 Review.
-
Identification of functional SNP associated with sperm quality in porcine ANXA5 that contributes to the growth of immature Sertoli cell.Front Vet Sci. 2025 May 14;12:1576566. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1576566. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40438404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Auharek S.A., Avelar G.F., Lara N.L., Sharpe R.M., França L.R. Sertoli cell numbers and spermatogenic efficiency are increased in inducible nitric oxide synthase mutant mice. Int. J. Androl. 2011;34:e621. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann M., Dierichs R. Postnatal formation of the blood-testis barrier in the rat with special reference to the initiation of meiosis. Anat. Embryol. 1983;168:269–275. - PubMed
-
- Beumer T.L., Kiyokawa H., Roepers-Gajadien H.L., van den Bos L.A., Lock T.M., Gademan I.S., Rutgers D.H., Koff A., de Rooij D.G. Regulatory role of CDKN1B in the mouse and human testis. Endocrinology. 1999;140:1834–1840. - PubMed
-
- Buzzard J.J., Wreford N.G., Morrison J.R. Thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and testosterone suppress proliferation and induce markers of differentiation in cultured rat Sertoli cells. Endocrinology. 2003;144:3722–3731. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

