The role of estrogen receptors in rat Sertoli cells at different stages of development
- PMID: 33163677
- PMCID: PMC7609458
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05363
The role of estrogen receptors in rat Sertoli cells at different stages of development
Abstract
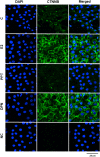
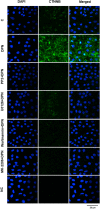
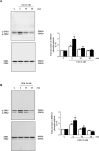
The aim of the study was to investigate the effects of estrogen receptors (ESR1 and ESR2) on the expression of the proteins involved with proliferation (CCND1) and differentiation (CDKN1B and CTNNB) of Sertoli cells from rat in different stages of development. ESR1-selective agonist PPT, but not ESR2-selective agonist DPN, increased CCND1 expression in Sertoli cells from 5- and 15-day old rats. PPT did not have any effect on CCND1 expression in Sertoli cells from 20- and 30-day-old rats. DPN, but not PPT, increased CDKN1B expression in Sertoli cells from 15-, 20-, 30-day-old rats. DPN did not have any effect on Sertoli cells from 5-day-old rats. 17β-estradiol (E2) and PPT enhanced the [Methyl-3H] thymidine incorporation in Sertoli cells from 15-day-old rats, whereas the treatment did not have any effect in 20-day-old rats. E2 and DPN, but not PPT, increased non-phosphorylated CTNNB expression in Sertoli cells from 20-day-old rats. This upregulation was blocked by ESR2-selective antagonist PHTPP. The activation of ESR1 and ESR2, respectively, plays a role in the proliferation and differentiation of Sertoli cells in a critical period of testicular development. Furthermore, in Sertoli cells from 20-day-old rats, upregulation of non-phosphorylated CTNNB by E2/ESR2, via c-SRC/ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT, may play a role in the interaction between Sertoli cells and/or in cell-germ cell adhesion and/or in the stabilization and accumulation of CTNNB in the cytosol. CTNNB could be translocated to the nucleus and modulate the transcriptional activity of specific target genes. The present study reinforces the important role of estrogen in normal testis development.
Keywords: 17β-estradiol; Cell biology; Cell culture; Cell differentiation; Estrogen receptors; Reproductive hormone; Reproductive medicine; Sertoli cells; Steroid hormones; Systems biology.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Figures







References
-
- Auharek S.A., Avelar G.F., Lara N.L., Sharpe R.M., França L.R. Sertoli cell numbers and spermatogenic efficiency are increased in inducible nitric oxide synthase mutant mice. Int. J. Androl. 2011;34:e621. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann M., Dierichs R. Postnatal formation of the blood-testis barrier in the rat with special reference to the initiation of meiosis. Anat. Embryol. 1983;168:269–275. - PubMed
-
- Beumer T.L., Kiyokawa H., Roepers-Gajadien H.L., van den Bos L.A., Lock T.M., Gademan I.S., Rutgers D.H., Koff A., de Rooij D.G. Regulatory role of CDKN1B in the mouse and human testis. Endocrinology. 1999;140:1834–1840. - PubMed
-
- Buzzard J.J., Wreford N.G., Morrison J.R. Thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and testosterone suppress proliferation and induce markers of differentiation in cultured rat Sertoli cells. Endocrinology. 2003;144:3722–3731. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

