Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Mortality Among Prevalent Hemodialysis Patients in the Japan Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study
- PMID: 33163716
- PMCID: PMC7609896
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2020.08.013
Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Mortality Among Prevalent Hemodialysis Patients in the Japan Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study
Abstract
Introduction: Elevated fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) levels have been strongly associated with mortality in the predialysis and incident hemodialysis populations, but few studies have examined this relationship in a large cohort of prevalent hemodialysis patients and in particular among persons with high dialysis vintage. To address this, we analyzed data from the Japan Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (J-DOPPS).
Methods: We included 1122 prevalent hemodialysis patients from the J-DOPPS phase 5 (2012-2015) who had FGF23 measurements. We evaluated the association of FGF23 levels with all-cause mortality and cardiovascular composite outcome using Cox regression adjusted for potential confounders.
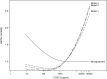
Results: At study enrollment, median dialysis vintage was 5.8 years (interquartile range, 2.7-12.4 years) and median FGF23 level was 2113 pg/ml (interquartile range, 583-6880 pg/ml). During 3-year follow-up, 154 of the 1122 participants died. In adjusted analyses, higher FGF23 was associated with a greater hazard of death (hazard ratio per doubling of FGF23, 1.12; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.21); however, the association became weaker as the dialysis vintage increased and finally disappeared in the highest tertile (>9.4 years). Similar patterns of effect modification by dialysis vintage were observed for cardiovascular composite outcome and in time-dependent models.
Conclusion: Elevated FGF23 was associated with mortality and cardiovascular events in prevalent hemodialysis patients, but the association was attenuated at longer dialysis vintages. This novel finding suggests that long-term hemodialysis patients may be less susceptible to the detrimental effects of FGF23 or correlated biological processes, and additional studies are needed to gain understanding of these possibilities.
Keywords: FGF23; hemodialysis; kidney failure; mortality.
© 2020 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Go A.S., Chertow G.M., Fan D. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1296–1305. - PubMed
-
- Komaba H., Fukagawa M. The role of FGF23 in CKD—with or without Klotho. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012;8:484–490. - PubMed
-
- Vervloet M. Renal and extrarenal effects of fibroblast growth factor 23. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018;15:109–120. - PubMed
-
- Shigematsu T., Kazama J.J., Yamashita T. Possible involvement of circulating fibroblast growth factor 23 in the development of secondary hyperparathyroidism associated with renal insufficiency. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;44:250–256. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

