Morphology-dependent titanium dioxide nanoparticle-induced keratinocyte toxicity and exacerbation of allergic contact dermatitis
- PMID: 33163967
- PMCID: PMC7643926
- DOI: 10.24966/tcr-3735/100019
Morphology-dependent titanium dioxide nanoparticle-induced keratinocyte toxicity and exacerbation of allergic contact dermatitis
Abstract
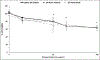
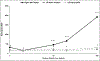
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles are commonly found in consumer products, such as sunscreens, and human dermal exposures are relatively high. Research suggests potential differences in the toxicity of anatase and rutile crystalline forms of TiO2. Additionally, transition metal dopants are frequently used to enhance physicochemical properties of TiO2, and the toxicity of these nanoparticles are not extensively studied. Therefore, this work examined the keratinocyte toxicity and in vivo skin allergy responses after treatment with 30 nm anatase, 30 nm rutile, or <100 nm Mn-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. After a 24-hour exposure, there were no differences in keratinocyte cytotoxicity; however, Mn-doped TiO2 nanoparticles induced significant in vitro ROS generation and in vivo skin swelling responses in a model of allergic contact dermatitis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Does photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles correspond to photo-cytotoxicity? Cellular uptake of TiO2 nanoparticles is important in their photo-cytotoxicity.Toxicol Mech Methods. 2016 May;26(4):284-94. doi: 10.1080/15376516.2016.1175530. Epub 2016 May 4. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2016. PMID: 27142467
-
Cytotoxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles to mussel hemocytes and gill cells in vitro: Influence of synthesis method, crystalline structure, size and additive.Nanotoxicology. 2015;9(5):543-53. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2014.952362. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Nanotoxicology. 2015. PMID: 25188678
-
Nano titanium dioxide induces the generation of ROS and potential damage in HaCaT cells under UVA irradiation.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2010 Dec;10(12):8500-7. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2010.2682. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2010. PMID: 21121359
-
Titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles in sunscreens: focus on their safety and effectiveness.Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2011 Oct 13;4:95-112. doi: 10.2147/NSA.S19419. Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2011. PMID: 24198489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in cosmetics.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Nov;33 Suppl 7:34-46. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15943. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019. PMID: 31588611 Review.
Cited by
-
An Overview of the Beneficial Role of Antioxidants in the Treatment of Nanoparticle-Induced Toxicities.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Nov 15;2021:7244677. doi: 10.1155/2021/7244677. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34820054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Effects of Nanoparticles on Dendritic Cells in a Model of Allergic Contact Dermatitis - Importance of PD-L2 Expression.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 12:rs.3.rs-3069059. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3069059/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 25;13(1):15992. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42797-5. PMID: 37503107 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Nanomaterial-Based Therapy for Wound Healing.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Feb 12;12(4):618. doi: 10.3390/nano12040618. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory effects of nanoparticles on dendritic cells in a model of allergic contact dermatitis: importance of PD-L2 expression.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 25;13(1):15992. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42797-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37749142 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vujovic M & Kostic E Titanium Dioxide and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Sunscreens: A Review of Toxicological Data. Journal of cosmetic science 70, 223–234 (2019). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
