Ensemble of CheXNet and VGG-19 Feature Extractor with Random Forest Classifier for Pediatric Pneumonia Detection
- PMID: 33163973
- PMCID: PMC7597433
- DOI: 10.1007/s42979-020-00373-y
Ensemble of CheXNet and VGG-19 Feature Extractor with Random Forest Classifier for Pediatric Pneumonia Detection
Abstract
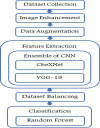
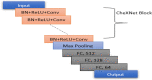
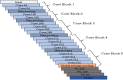
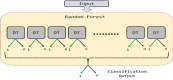
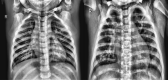
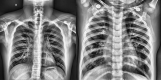
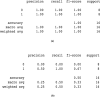
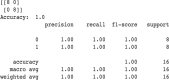
Pneumonia, an acute respiratory infection, causes serious breathing hindrance by damaging lung/s. Recovery of pneumonia patients depends on the early diagnosis of the disease and proper treatment. This paper proposes an ensemble method-based pneumonia diagnosis from Chest X-ray images. The deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)-CheXNet and VGG-19 are trained and used to extract features from given X-ray images. These features are then ensembled for classification. To overcome data irregularity problem, Random Under Sampler (RUS), Random Over Sampler (ROS) and Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) are applied on the ensembled feature vector. The ensembled feature vector is then classified using several Machine Learning (ML) classification techniques (Random Forest, Adaptive Boosting, K-Nearest Neighbors). Among these methods, Random Forest got better performance metrics than others on the available standard dataset. Comparison with existing methods shows that the proposed method attains improved classification accuracy, AUC values and outperforms all other models providing 98.93% accurate prediction. The model also exhibits potential generalization capacity when tested on different dataset. Outcomes of this study can be great to use for pneumonia diagnosis from chest X-ray images.
Keywords: AUC; Convolutional neural network; Ensemble method; Machine learning; Pneumonia; SMOTE.
© Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stacked ensemble learning based on deep convolutional neural networks for pediatric pneumonia diagnosis using chest X-ray images.Neural Comput Appl. 2023;35(11):8259-8279. doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-08099-z. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Neural Comput Appl. 2023. PMID: 36532883 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of Pediatric Pneumonia with Ensemble of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks in Chest X-Ray Images.Arab J Sci Eng. 2022;47(2):2123-2139. doi: 10.1007/s13369-021-06127-z. Epub 2021 Sep 12. Arab J Sci Eng. 2022. PMID: 34540526 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid Stacking-SMOTE model for optimizing the prediction of autistic genes.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Oct 6;24(1):379. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05501-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 37803253 Free PMC article.
-
Handling class imbalance in COVID-19 chest X-ray images classification: Using SMOTE and weighted loss.Appl Soft Comput. 2022 Nov;129:109588. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2022.109588. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Appl Soft Comput. 2022. PMID: 36061418 Free PMC article.
-
Data-driven classification and explainable-AI in the field of lung imaging.Front Big Data. 2024 Sep 19;7:1393758. doi: 10.3389/fdata.2024.1393758. eCollection 2024. Front Big Data. 2024. PMID: 39364222 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Semi-ProtoPNet Deep Neural Network for the Classification of Defective Power Grid Distribution Structures.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 27;22(13):4859. doi: 10.3390/s22134859. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808353 Free PMC article.
-
Design ensemble deep learning model for pneumonia disease classification.Int J Multimed Inf Retr. 2021;10(1):55-68. doi: 10.1007/s13735-021-00204-7. Epub 2021 Feb 20. Int J Multimed Inf Retr. 2021. PMID: 33643764 Free PMC article.
-
Stacked ensemble learning based on deep convolutional neural networks for pediatric pneumonia diagnosis using chest X-ray images.Neural Comput Appl. 2023;35(11):8259-8279. doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-08099-z. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Neural Comput Appl. 2023. PMID: 36532883 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumonia detection with QCSA network on chest X-ray.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 3;13(1):9025. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35922-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37270553 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric chest radiograph interpretation: how far has artificial intelligence come? A systematic literature review.Pediatr Radiol. 2022 Jul;52(8):1568-1580. doi: 10.1007/s00247-022-05368-w. Epub 2022 Apr 23. Pediatr Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35460035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- CDC, 2017. https://www.cdc.gov/dotw/pneumonia/index.html. Accessed 22 July 2020.
-
- F. Online, 17 lakh Indian children to die due to pneumonia by 2030; here’s how it can be averted. 2018. https://www.financialexpress.com/economy/17-lakh-indian-children-to-die-....
-
- Deepa NV, Krishna N, Kumar GH. Feature extraction and classification of X-ray lung images using haralick texture features. Singapore: Springer Nature; 2018. pp. 899–907.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
