Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction diminishes peripheral hemodynamics and accelerates exercise-induced neuromuscular fatigue
- PMID: 33164549
- PMCID: PMC7847082
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00266.2020
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction diminishes peripheral hemodynamics and accelerates exercise-induced neuromuscular fatigue
Abstract
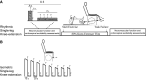
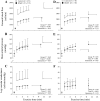
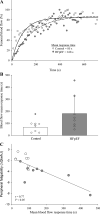
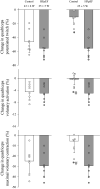
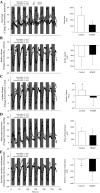
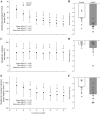
This study investigated the impact of HFpEF on neuromuscular fatigue and peripheral hemodynamics during small muscle mass exercise not limited by cardiac output. Eight HFpEF patients (NYHA II-III, ejection-fraction: 61 ± 2%) and eight healthy controls performed dynamic knee extension exercise (80% peak workload) to task failure and maximal intermittent quadriceps contractions (8 × 15 s). Controls repeated knee extension at the same absolute intensity as HFpEF. Leg blood flow (QL) was quantified using Doppler ultrasound. Pre/postexercise changes in quadriceps twitch torque (ΔQtw; peripheral fatigue), voluntary activation (ΔVA; central fatigue), and corticospinal excitability were quantified. At the same relative intensity, HFpEF (24 ± 5 W) and controls (42 ± 6 W) had a similar time-to-task failure (∼10 min), ΔQtw (∼50%), and ΔVA (∼6%). This resulted in a greater exercise-induced change in neuromuscular function per unit work in HFpEF, which was significantly correlated with a slower QL response time. Knee extension exercise at the same absolute intensity resulted in an ∼40% lower QL and greater ΔQtw and ΔVA in HFpEF than in controls. Corticospinal excitability remained unaltered during exercise in both groups. Finally, despite a similar ΔVA, ΔQtw was larger in HFpEF versus controls during isometric exercise. In conclusion, HFpEF patients are characterized by a similar development of central and peripheral fatigue as healthy controls when tested at the same relative intensity during exercise not limited by cardiac output. However, HFpEF patients have a greater susceptibility to neuromuscular fatigue during exercise at a given absolute intensity, and this impairs functional capacity. The patients' compromised QL response to exercise likely accounts, at least partly, for the patients' attenuated fatigue resistance.NEW & NOTEWORTHY The susceptibility to neuromuscular fatigue during exercise is substantially exaggerated in individuals with heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. The faster rate of fatigue development is associated with the compromised peripheral hemodynamic response characterizing these patients during exercise. Given the role of neuromuscular fatigue as a factor limiting exercise, this impairment likely accounts for a significant portion of the exercise intolerance typical for this population.
Keywords: exercise intolerance; fatigue; heart failure; hemodynamics.
Figures
References
-
- Borlaug BA, Melenovsky V, Russell SD, Kessler K, Pacak K, Becker LC, Kass DA. Impaired chronotropic and vasodilator reserves limit exercise capacity in patients with heart failure and a preserved ejection fraction. Circulation 114: 2138–2147, 2006. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.632745. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kitzman DW, Nicklas B, Kraus WE, Lyles MF, Eggebeen J, Morgan TM, Haykowsky M. Skeletal muscle abnormalities and exercise intolerance in older patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 306: H1364–H1370, 2014. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00004.2014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Parthasarathy HK, Pieske B, Weisskopf M, Andrews CD, Brunel P, Struthers AD, MacDonald TM. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to determine the effects of valsartan on exercise time in patients with symptomatic heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur J Heart Fail 11: 980–989, 2009. doi:10.1093/eurjhf/hfp120. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

