Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Attenuate Infection-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Animal Experiments: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33164559
- PMCID: PMC7784610
- DOI: 10.1177/0963689720969186
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Attenuate Infection-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Animal Experiments: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
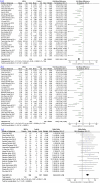
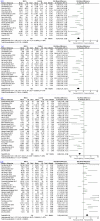
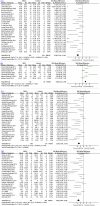
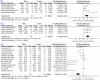
Mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) therapy is a potential therapy for treating acute lung injury (ALI) or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which was widely studied in the last decade. The purpose of our meta-analysis was to investigate the efficacy of MSCs for simulated infection-induced ALI/ARDS in animal trials. PubMed and EMBASE were searched to screen relevant preclinical trials with a prespecified search strategy. 57 studies met the inclusion criteria and were included in our study. Our meta-analysis showed that MSCs can reduce the lung injury score of ALI caused by lipopolysaccharide or bacteria (standardized mean difference (SMD) = -2.97, 95% CI [-3.64 to -2.30], P < 0.00001) and improve the animals' survival (odds ratio = 3.64, 95% CI [2.55 to 5.19], P < 0.00001). Our study discovered that MSCs can reduce the wet weight to dry weight ratio of the lung (SMD = -2.58, 95% CI [-3.24 to -1.91], P < 0.00001). The proportion of the alveolar sac in the MSC group was higher than that in the control group (SMD = 1.68, 95% CI [1.22 to 2.13], P < 0.00001). Moreover, our study detected that MSCs can downregulate the levels of proinflammatory factors such as interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α in the lung and it can upregulate the level of anti-inflammatory factor IL-10. MSCs were also found to reduce the level of neutrophils and total protein in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, decrease myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity in the lung, and improve lung compliance. MSC therapy may be a promising treatment for ALI/ARDS since it may mitigate the severity of lung injury, modulate the immune balance, and ameliorate the permeability of lung vessels in ALI/ARDS, thus facilitating lung regeneration and repair.
Keywords: acute lung injury; acute respiratory distress syndrome; cell therapy; mesenchymal stromal cell; stem cell.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Force ADT, Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, Ferguson ND, Caldwell E. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the berlin definition. JAMA. 2012;307(23):2526–2533. - PubMed
-
- Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, Fan E, Brochard L, Esteban A, Gattinoni L, Van Haren F, Larsson A, McAuley DF, Ranieri M, et al. Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries. JAMA. 2016;315(8):788–800. - PubMed
-
- Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhyan RK, Latsinik NV, Panasyuk AF, Keiliss-Borok IV. Stromal cells responsible for transferring the microenvironment of the hemopoietic tissues. Cloning in vitro and retransplantation in vivo. Transplantation. 1974;17(4):331–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

