Large artery stiffness and brain health: insights from animal models
- PMID: 33164578
- PMCID: PMC7847068
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00696.2020
Large artery stiffness and brain health: insights from animal models
Abstract
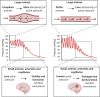
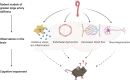
There are no effective treatments available to halt or reverse the progression of age-related cognitive decline and Alzheimer's disease. Thus, there is an urgent need to understand the underlying mechanisms of disease etiology and progression to identify novel therapeutic targets. Age-related changes to the vasculature, particularly increases in stiffness of the large elastic arteries, are now recognized as important contributors to brain aging. There is a growing body of evidence for an association between greater large artery stiffness and cognitive impairment among both healthy older adults and patients with Alzheimer's disease. However, studies in humans are limited to only correlative evidence, whereas animal models allow researchers to explore the causative mechanisms linking arterial stiffness to neurocognitive dysfunction and disease. Recently, several rodent models of direct modulation of large artery stiffness and the consequent effects on the brain have been reported. Common outcomes among these models have emerged, including evidence that greater large artery stiffness causes cerebrovascular dysfunction associated with increased oxidative stress and inflammatory signaling. The purpose of this mini-review is to highlight the recent findings associating large artery stiffness with deleterious brain outcomes, with a specific focus on causative evidence obtained from animal models. We will also discuss the gaps in knowledge that remain in our understanding of how large artery stiffness affects brain function and disease outcomes.
Keywords: aging; cerebrovascular; cognitive dysfunction; endothelial function; vascular stiffness.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of pulse pressure on cerebrovascular events leading to age-related cognitive decline.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Jun 1;314(6):H1214-H1224. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00637.2017. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29451817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arterial Stiffness Due to Carotid Calcification Disrupts Cerebral Blood Flow Regulation and Leads to Cognitive Deficits.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 May 7;8(9):e011630. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011630. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31057061 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological Continuum From the Rise in Pulse Pressure to Impaired Neurovascular Coupling and Cognitive Decline.Am J Hypertens. 2020 Apr 29;33(5):375-390. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpaa001. Am J Hypertens. 2020. PMID: 32202623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arterial stiffness, cognitive impairment and dementia: confounding factor or real risk?J Neurochem. 2018 Mar;144(5):527-548. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14235. Epub 2017 Nov 27. J Neurochem. 2018. PMID: 28991365 Review.
-
Impact of arterial stiffness on cerebrovascular function: a review of evidence from humans and preclincal models.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024 Mar 1;326(3):H689-H704. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00592.2023. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38214904 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Selective vulnerability of medial temporal regions to short-term blood pressure variability and cerebral hypoperfusion in older adults.Neuroimage Rep. 2022 Mar;2(1):100080. doi: 10.1016/j.ynirp.2022.100080. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Neuroimage Rep. 2022. PMID: 35784272 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Arterial Stiffness Index and Brain Structure in the UK Biobank: A 10-Year Retrospective Analysis.Aging Dis. 2024 Aug 1;15(4):1872-1884. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.0419. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 37307821 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular aging: spotlight on mitochondria.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024 Feb 1;326(2):H317-H333. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00632.2023. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38038719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of High Fat Diet on Cerebrovascular Health and Pathology: A Species Comparative Review.Molecules. 2021 Jun 4;26(11):3406. doi: 10.3390/molecules26113406. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34199898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerebrovascular microRNA Expression Profile During Early Development of Alzheimer's Disease in a Mouse Model.J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;85(1):91-113. doi: 10.3233/JAD-215223. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022. PMID: 34776451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kramarow EA, Tejada-Vera B. Dementia mortality in the United States 2000–2017. Natl Vital Stat Rep 68: 1–29, 2019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

