Diagnostic Accuracy of Nipple Aspirate Fluid Cytology in Asymptomatic Patients: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review of the Literature
- PMID: 33165721
- PMCID: PMC8184724
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-020-09313-9
Diagnostic Accuracy of Nipple Aspirate Fluid Cytology in Asymptomatic Patients: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review of the Literature
Abstract
Purpose: To calculate the diagnostic accuracy of nipple aspirate fluid (NAF) cytology.
Background: Evaluation of NAF cytology in asymptomatic patients conceptually offers a non-invasive method for either screening for breast cancer or else predicting or stratifying future cancer risk.
Methods: Studies were identified by performing electronic searches up to August 2019. A meta-analysis was conducted to attain an overall pooled sensitivity and specificity of NAF for breast cancer detection.
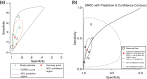
Results: A search through 938 studies yielded a total of 19 studies. Overall, 9308 patients were examined, with cytology results from 10,147 breasts [age (years), mean ± SD = 49.73 ± 4.09 years]. Diagnostic accuracy meta-analysis of NAF revealed a pooled specificity of 0.97 (95% CI 0.97-0.98), and sensitivity of 0.64 (95% CI 0.62-0.66).
Conclusions: The diagnostic accuracy of nipple smear cytology is limited by poor sensitivity. If nipple fluid assessment is to be used for diagnosis, then emerging technologies for fluid biomarker analysis must supersede the current diagnostic accuracy of NAF cytology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ASO Author Reflections: Diagnostic Accuracy of Nipple Aspirate Fluid Cytology in Asymptomatic Patients and Its Predictive Validity on Future Risk of Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of the Literature.Ann Surg Oncol. 2021 Jul;28(7):3761-3762. doi: 10.1245/s10434-020-09355-z. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33206265 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Nipple aspirate fluid cytology in breast carcinoma.Cancer. 2003 Apr 25;99(2):97-104. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10958. Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12704689
-
Nipple aspirate fluid and ductoscopy to detect breast cancer.Diagn Cytopathol. 2010 Apr;38(4):244-51. doi: 10.1002/dc.21177. Diagn Cytopathol. 2010. PMID: 19795490 Free PMC article.
-
Nipple aspirate fluid cytology and the Gail model for breast cancer risk assessment in a screening population.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005 Feb;14(2):324-8. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-04-0289. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005. PMID: 15734953
-
Accuracy for cytological evaluation in the detection of breast cancer among patients with pathologic nipple discharge: a PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2020 Feb 20;133(4):435-443. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000643. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020. PMID: 31977561 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The diagnostic value of cytology in the mammary intraductal lesions of patients with pathological nipple discharge.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 25;15(1):3243. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86533-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39863629 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the Intake of Isoflavones on Risk Factors of Breast Cancer-A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Intervention Studies.Nutrients. 2021 Jul 5;13(7):2309. doi: 10.3390/nu13072309. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34371819 Free PMC article.
-
Nipple Aspirate Fluid at a Glance.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 29;14(1):159. doi: 10.3390/cancers14010159. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35008326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nipple aspirate fluid and its use for the early detection of breast cancer.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Apr 18;77:103625. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103625. eCollection 2022 May. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35638006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The changing microRNA landscape by color and cloudiness: a cautionary tale for nipple aspirate fluid biomarker analysis.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021 Dec;44(6):1339-1349. doi: 10.1007/s13402-021-00641-w. Epub 2021 Oct 16. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021. PMID: 34655415 Free PMC article.
References
-
- West Midlands Cancer Intelligence Unit. Breast Cancer Clinical Outcome Measures (BCCOM) Project. 2007. https://associationofbreastsurgery.org.uk/media/63921/final-bccom_ar07_p.... - PubMed
-
- Dixon JM, Barber M. Breast Surgery: A Companion to Specialist Surgical Practice, Sixth Edition. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2018.
-
- Cancer Research UK. Breast Cancer Statistics. 2015.
-
- Martin JE, Moskowitz M, Milbrath JR. Breast cancer missed by mammography. Am J Roentgenol. 1979;132(5):737–739. - PubMed
-
- Majid AS, de Paredes ES, Doherty RD, Sharma NR, Salvador X. Missed breast carcinoma: pitfalls and pearls. Radiographics. 2003;23(4):881–895. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

